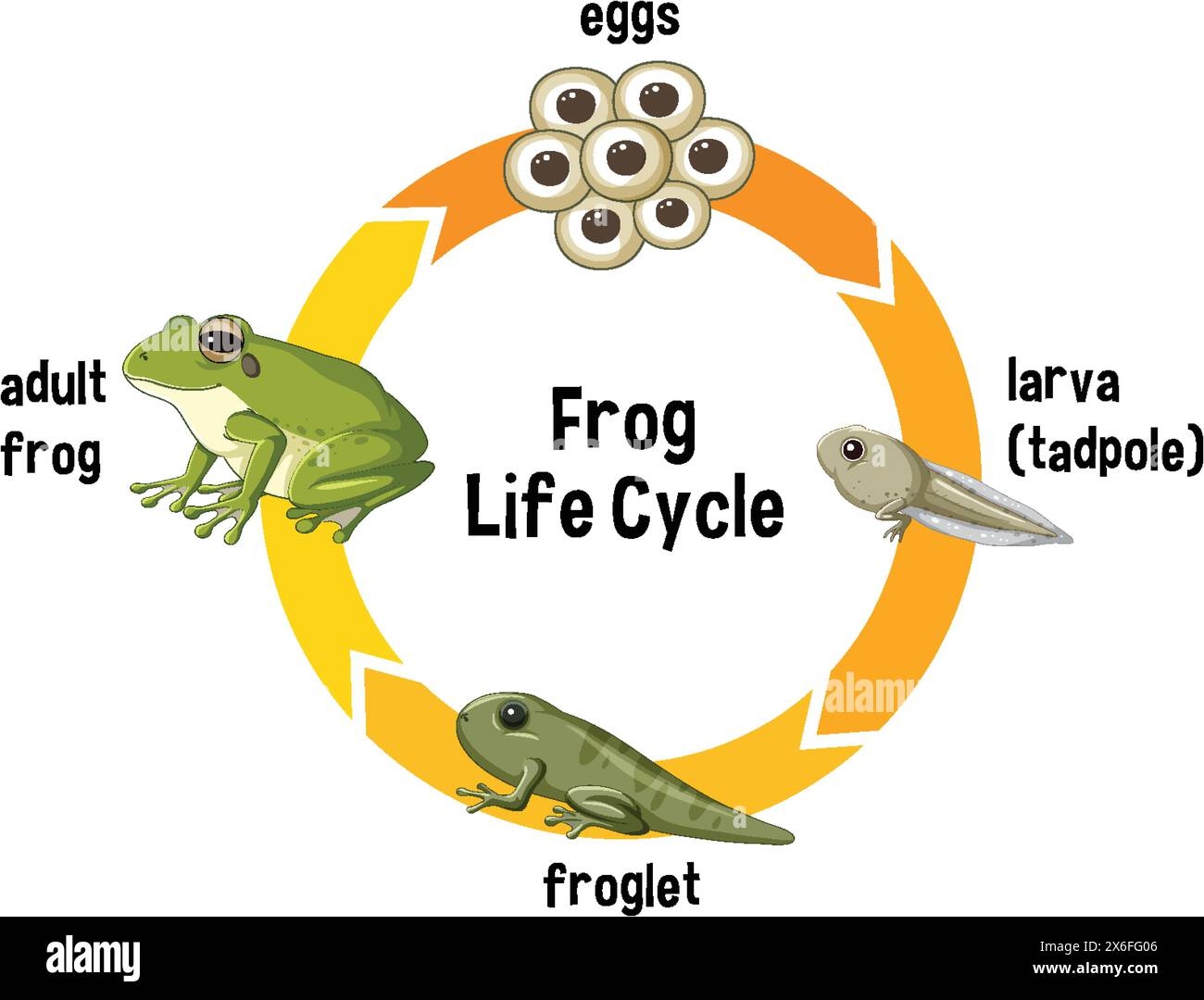
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through a remarkable transformation in their life cycle. From tiny tadpoles to hopping amphibians, the journey of a frog is truly amazing to witness. In this article, we will explore the 5 stages of a frog’s life cycle, from egg to adult.
5 Stages of a Frog
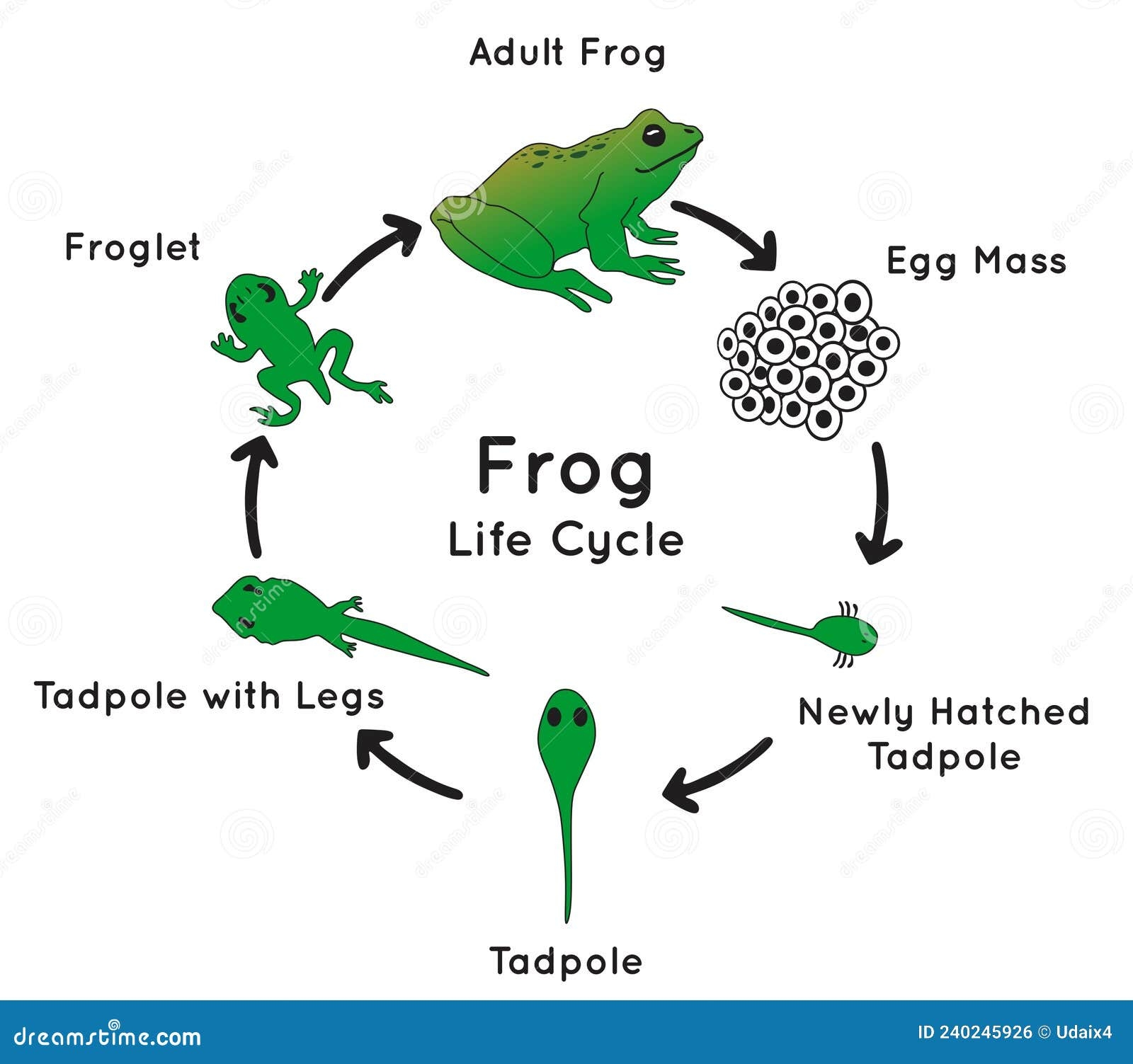
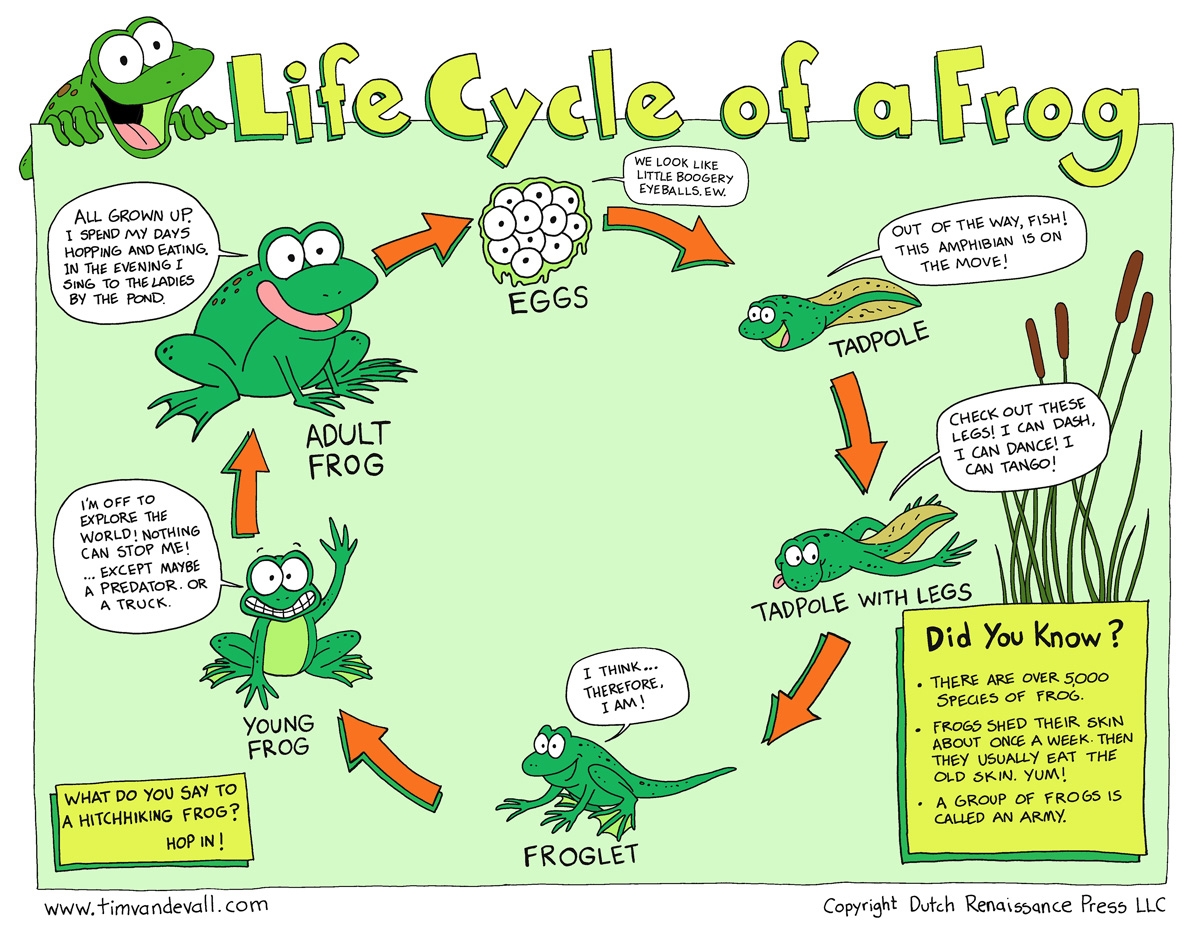
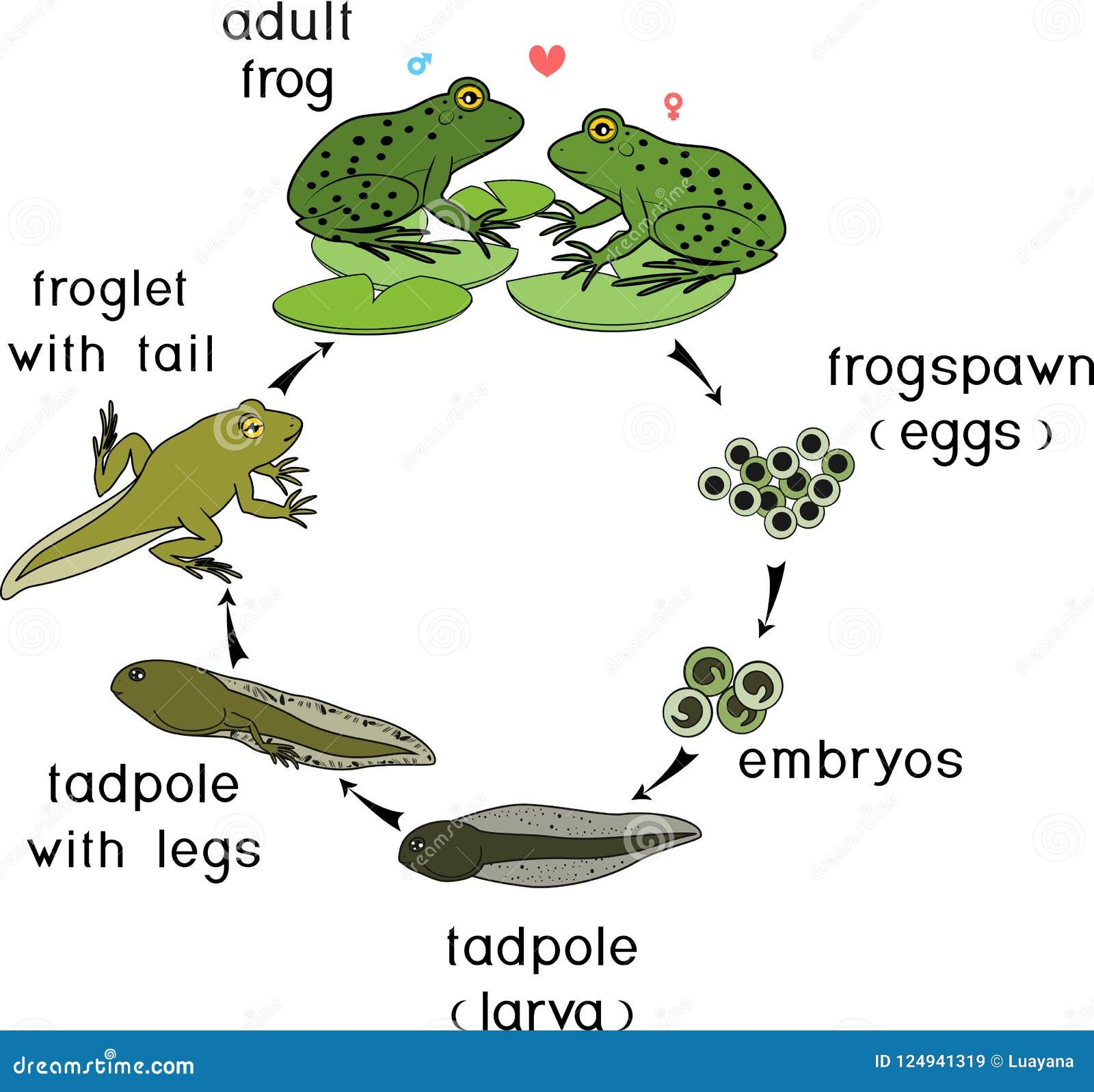
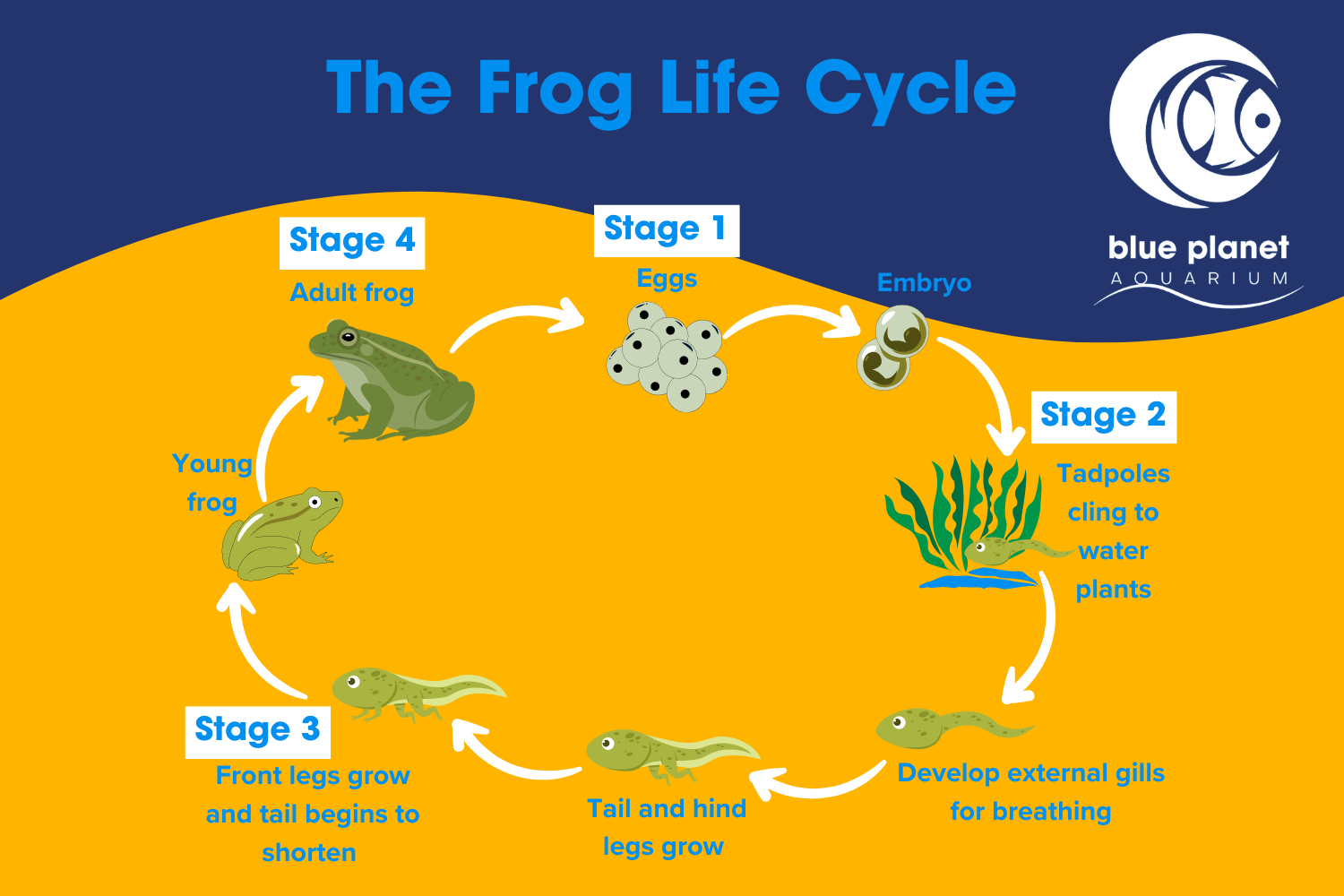
The first stage of a frog’s life cycle begins with an egg. Female frogs lay their eggs in water, and these eggs hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles are small, aquatic creatures with gills that help them breathe underwater. They feed on algae and other plant matter.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo a process called metamorphosis. During this stage, tadpoles develop hind legs, followed by front legs. Their tails gradually disappear as they transform into adult frogs. This transformation can take several weeks to months, depending on the species of frog.
Once the metamorphosis is complete, the young frog emerges from the water onto land. At this stage, the frog is known as a juvenile. Juvenile frogs have fully developed lungs that allow them to breathe air. They continue to grow and mature, eventually reaching adulthood.
Adult frogs are fully grown and capable of reproducing. They spend their time both on land and in water, depending on the species. Frogs are cold-blooded animals, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. They are also known for their unique ability to jump long distances.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a fascinating journey that showcases nature’s incredible diversity. From tiny eggs to hopping adults, each stage of a frog’s life is filled with wonder and beauty. Next time you see a frog, take a moment to appreciate the incredible transformation it has undergone to reach adulthood.