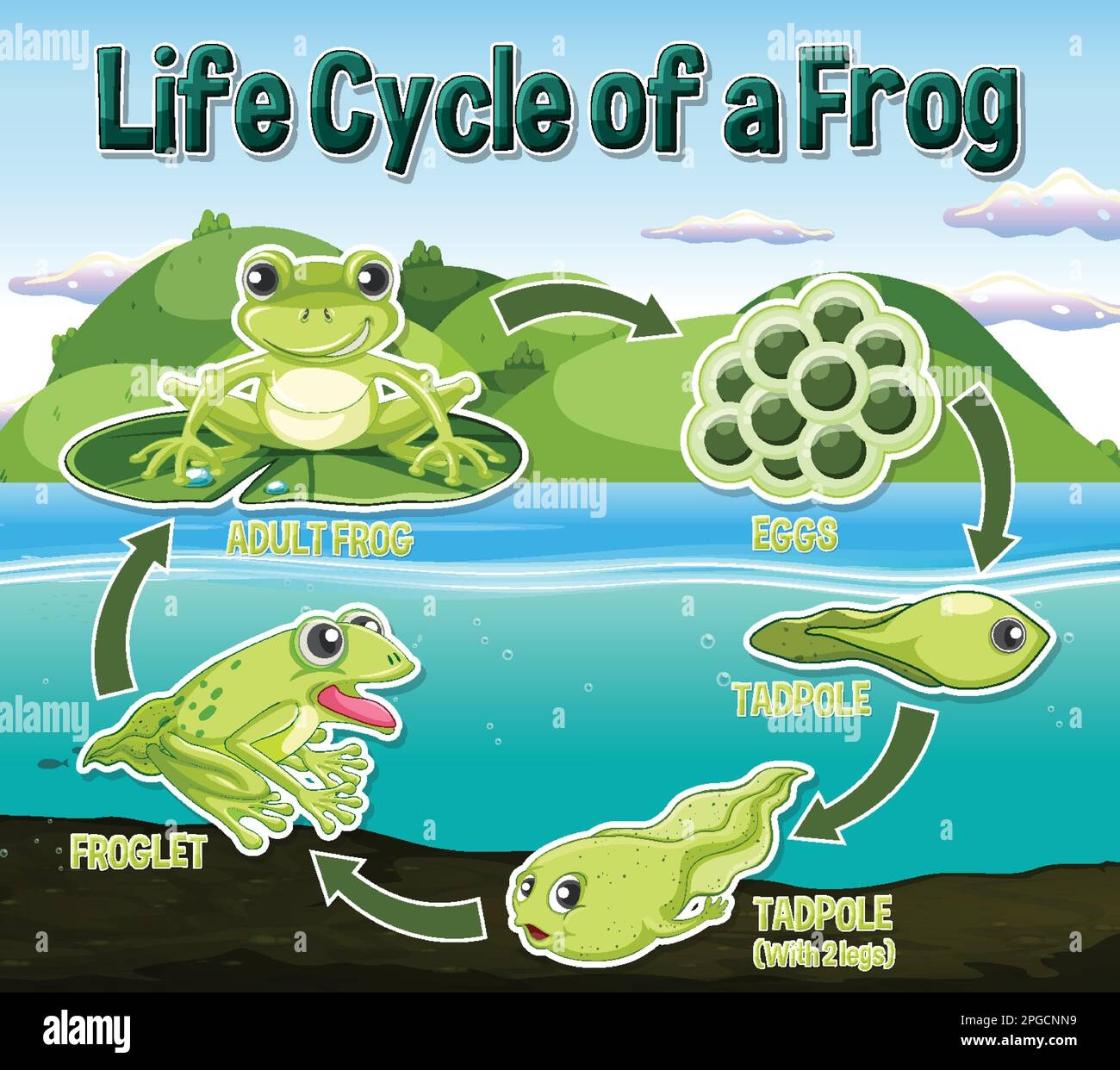
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through a unique life cycle. From tiny tadpoles to hopping adults, the journey of a frog is truly amazing to witness in nature. Let’s dive into the stages of the life cycle of a frog.
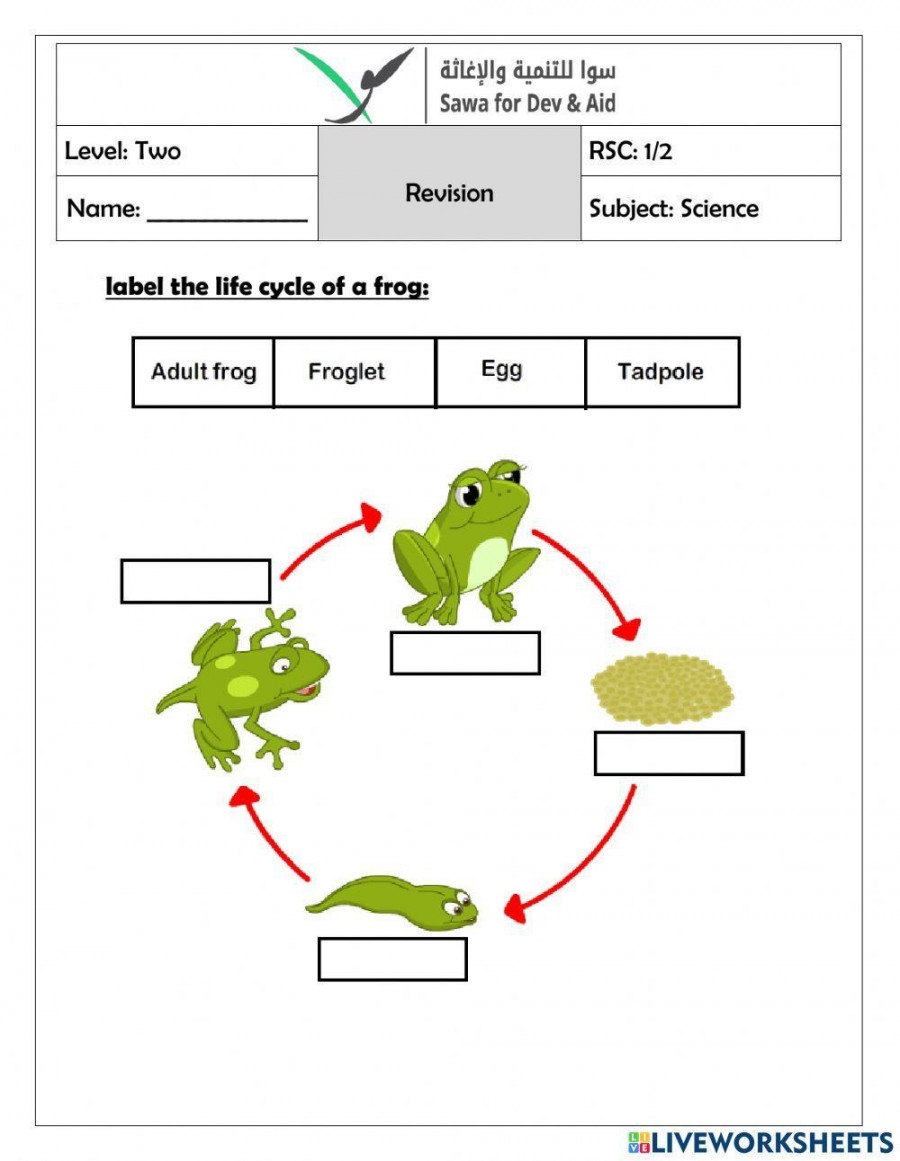
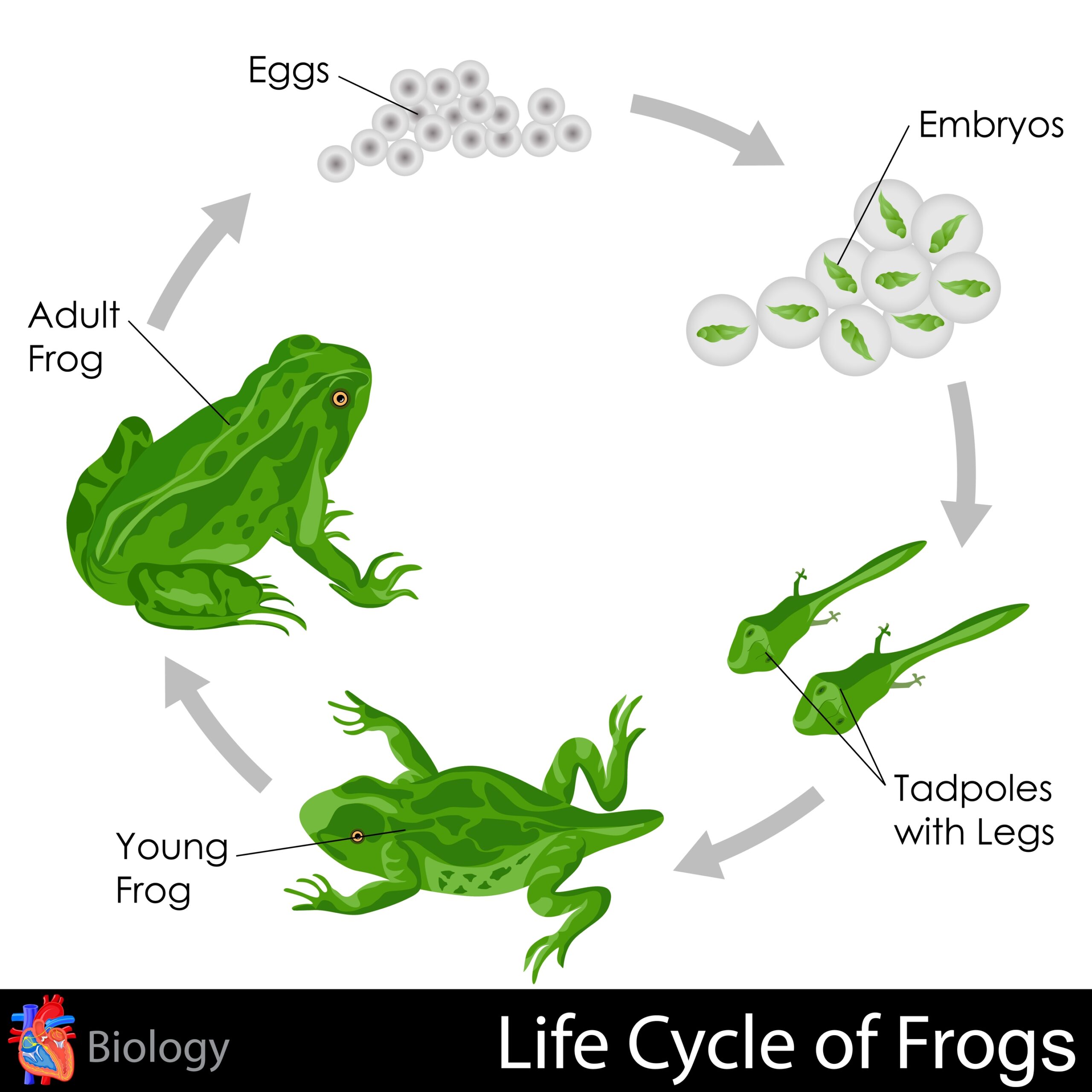
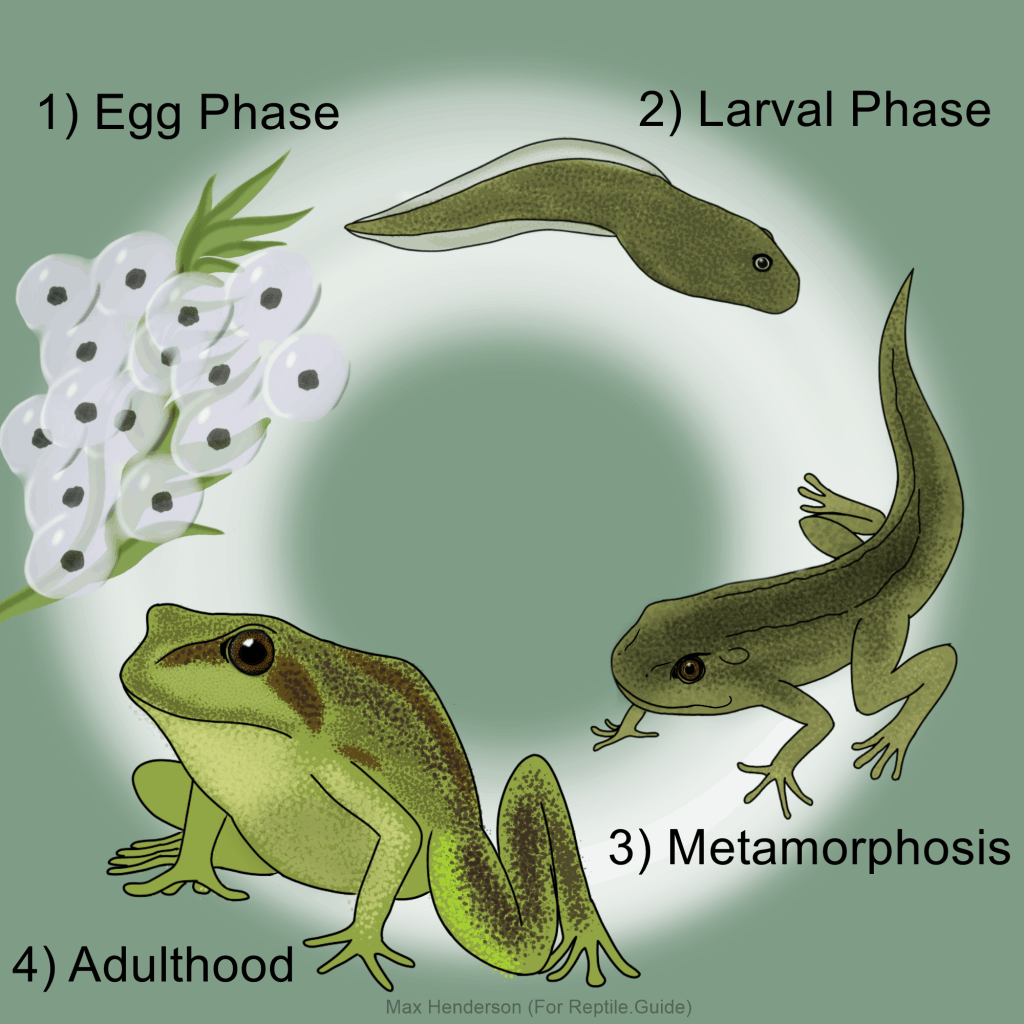
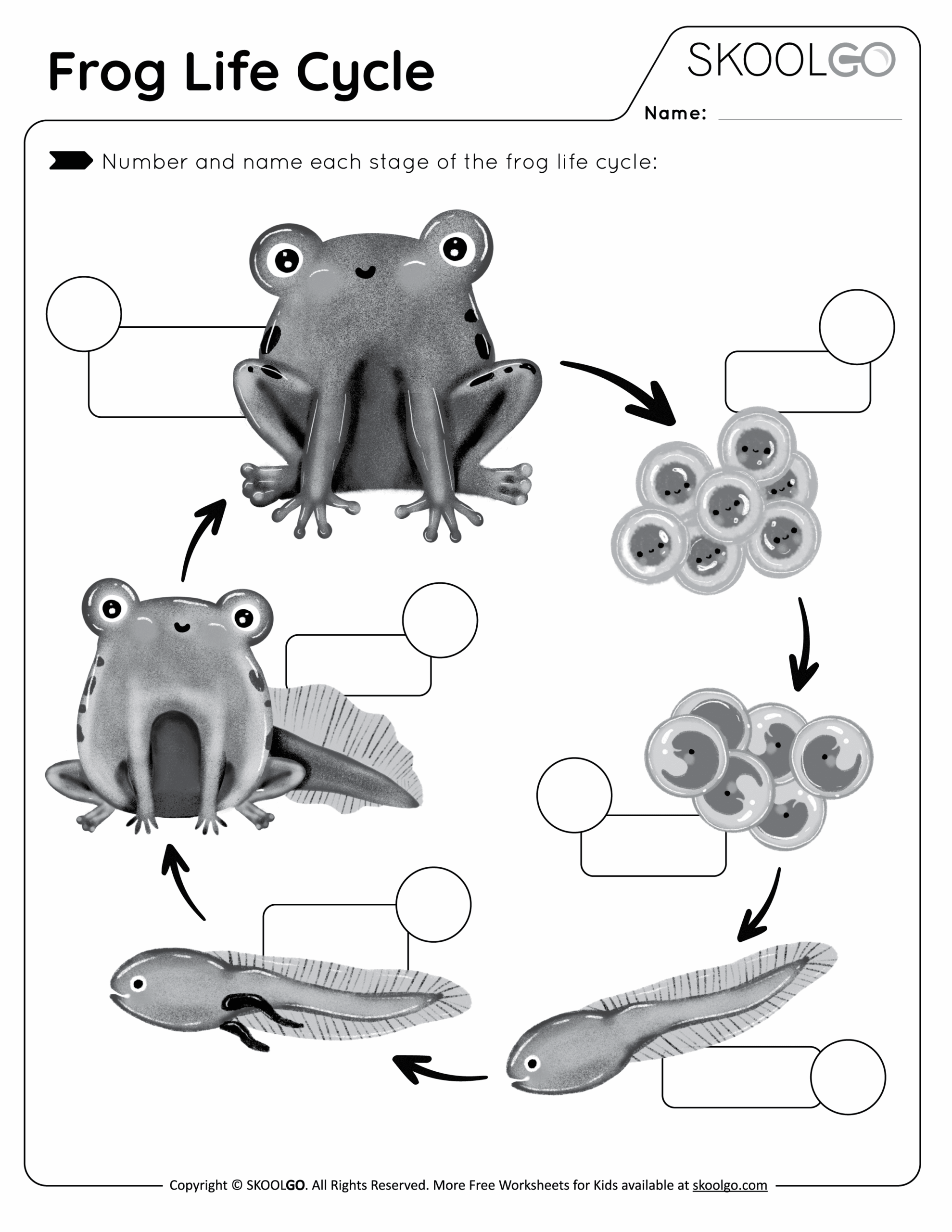
The life cycle of a frog
Frogs start their life as eggs laid in water by adult frogs. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which have gills for breathing underwater. As tadpoles grow, they develop legs and lose their tails, eventually transforming into froglets.
Once the froglets have fully developed into adult frogs, they leave the water to live on land. Adult frogs have lungs for breathing air and powerful hind legs for jumping. They also have sticky tongues for catching insects, their main source of food.
Frogs play an important role in the ecosystem as both predators and prey. They help control insect populations by eating pests like mosquitoes, while also serving as food for birds, fish, and other animals. Their presence indicates a healthy environment.
As amphibians, frogs are sensitive to changes in their habitat. Pollution, deforestation, and climate change can threaten their survival. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these fascinating creatures and maintain the balance of nature.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a remarkable journey from egg to adult. By understanding and appreciating the stages of their development, we can better appreciate the vital role that frogs play in the ecosystem. Let’s continue to support conservation efforts to ensure the survival of these fascinating amphibians.