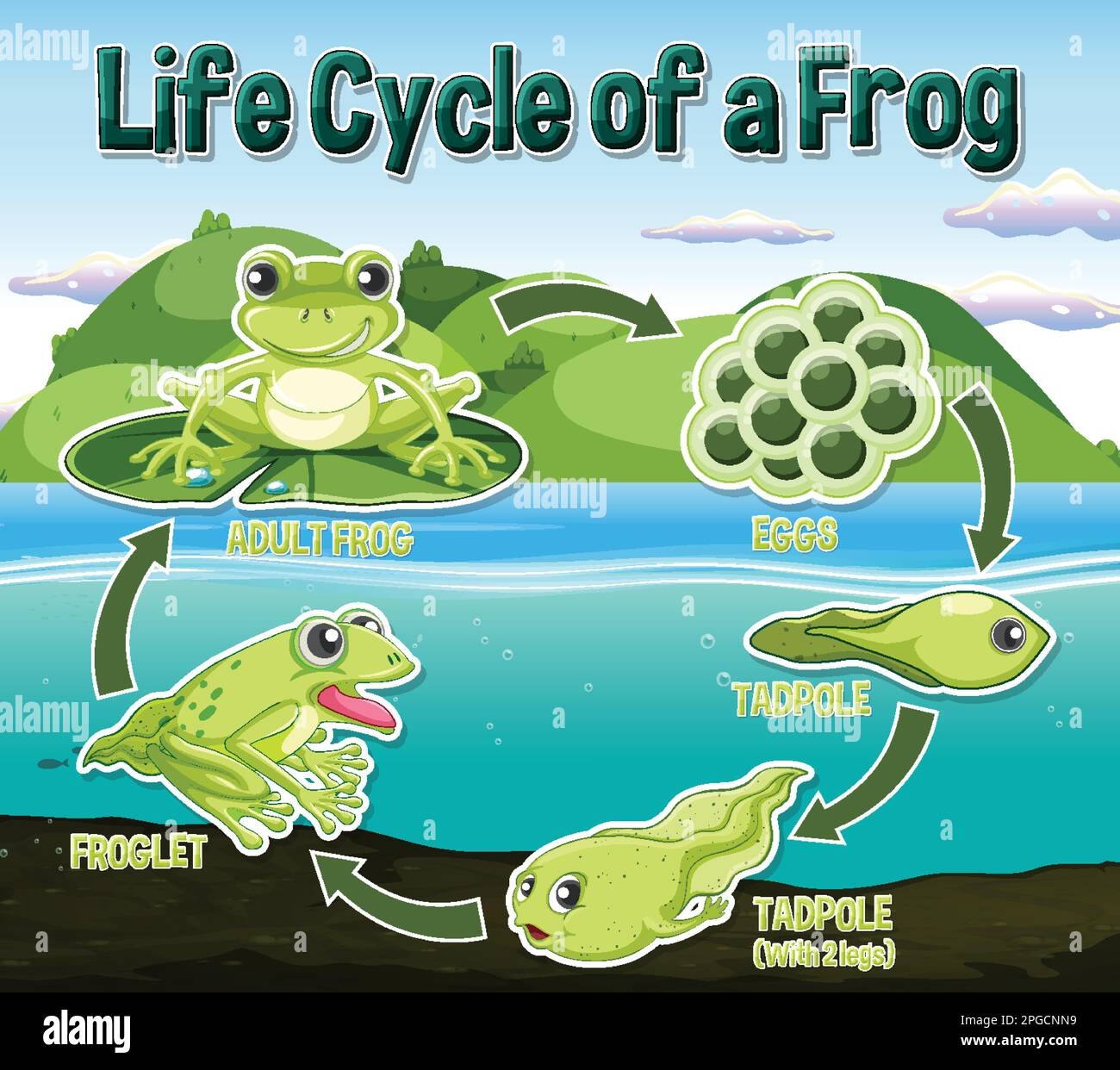
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through various stages in their life cycle. Understanding the life cycle of a frog can help us appreciate and protect these amphibians in their natural habitats.
From egg to tadpole to adult frog, each stage in the life cycle of a frog is unique and essential for its survival. Let’s dive into the details of the life cycle of a frog and explore how these amazing creatures transform over time.
Life Cycle of Frog Outline
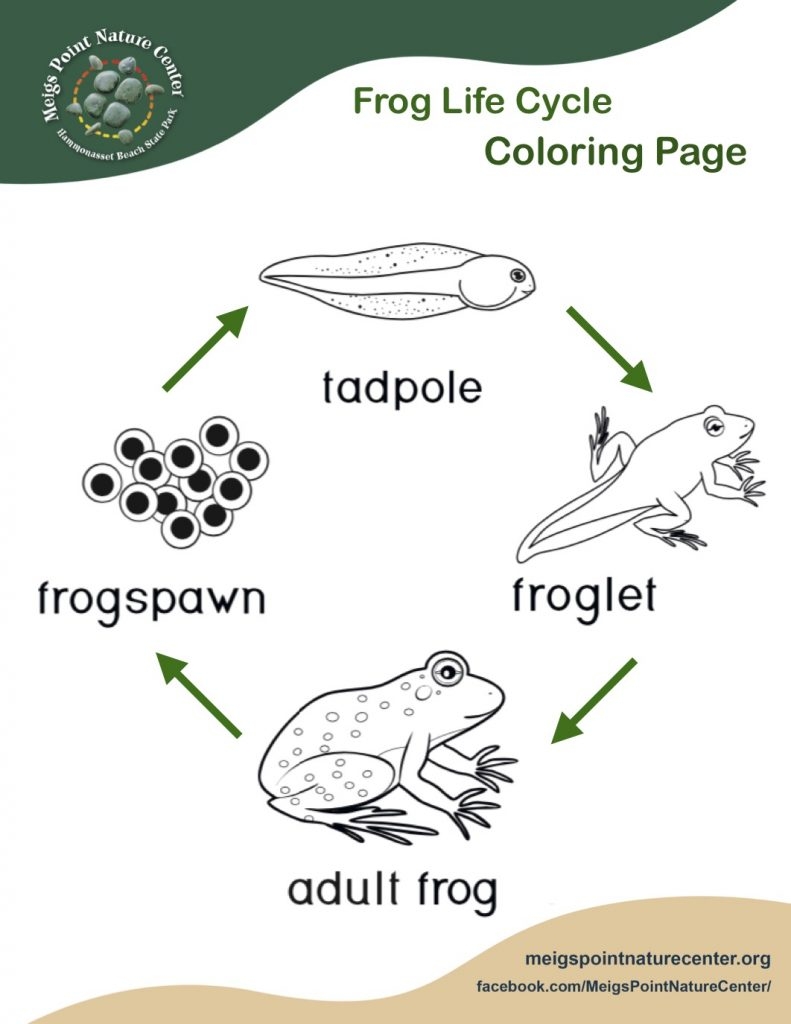
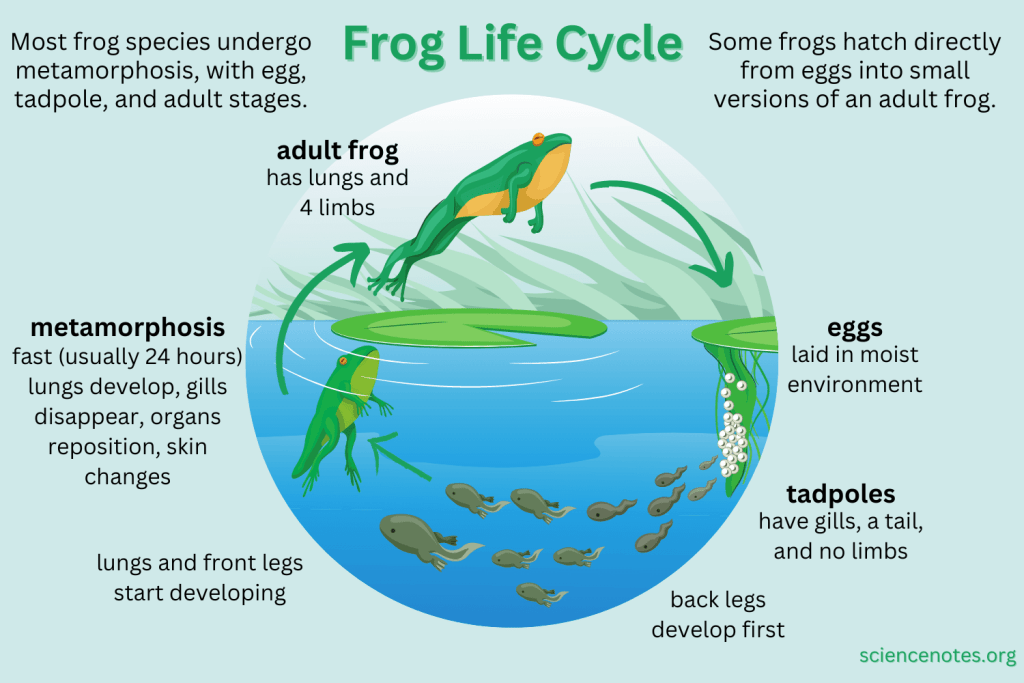
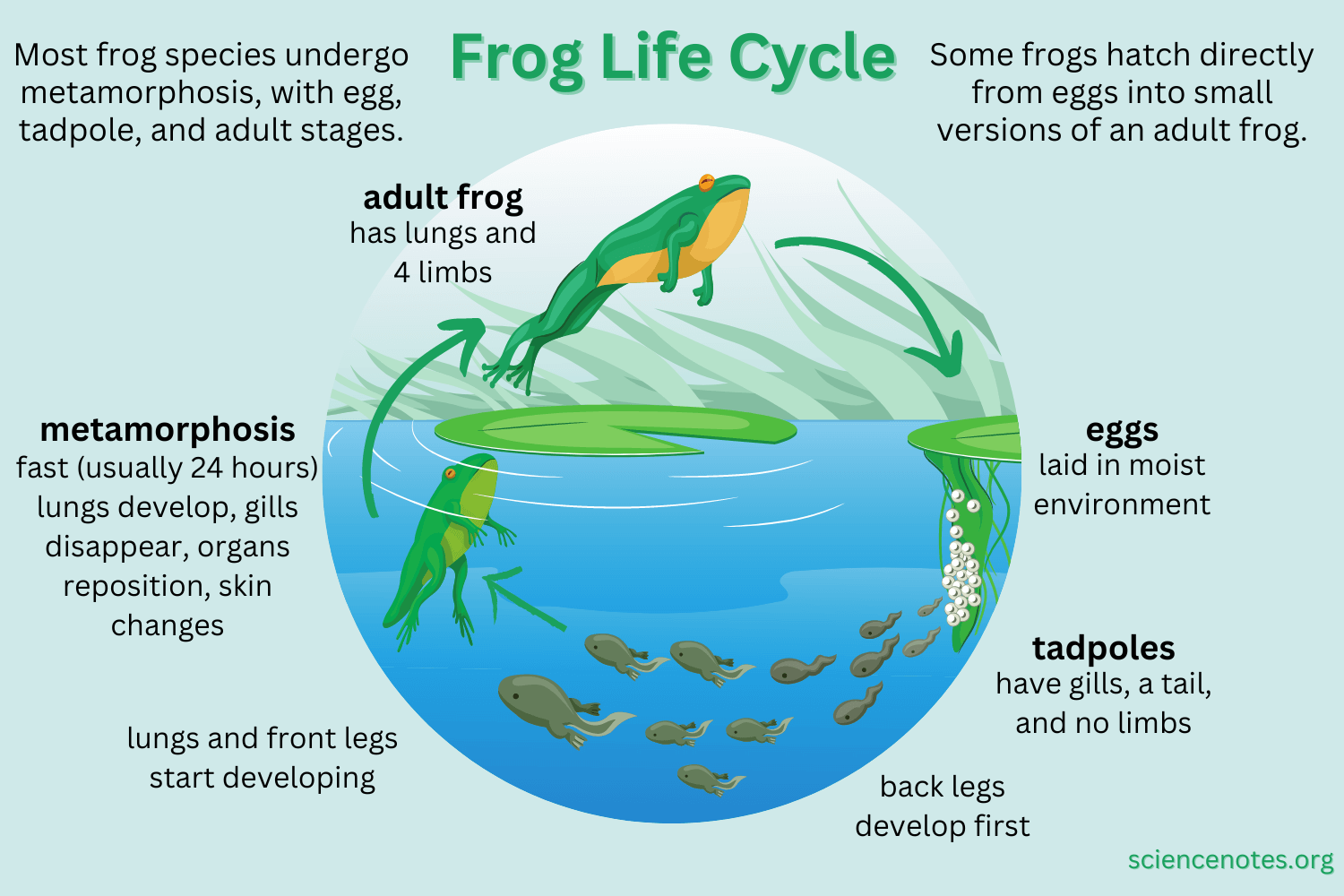
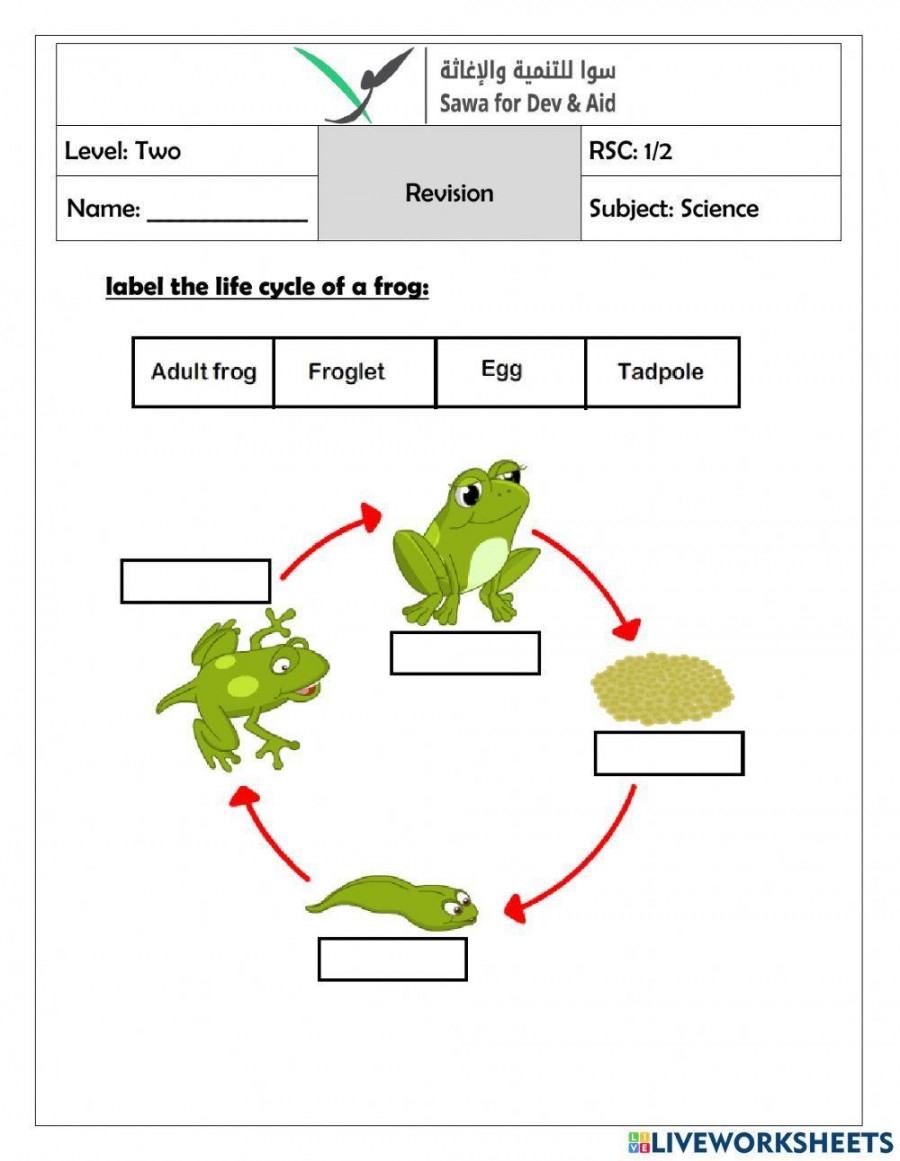
The life cycle of a frog begins with the laying of eggs in water by adult frogs. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which have gills for breathing underwater. Tadpoles feed on algae and grow rapidly during this stage.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo metamorphosis, developing lungs and limbs. Their tails are absorbed, and they start to resemble adult frogs. This transformation is crucial for their transition from water to land.
Once the transformation is complete, tadpoles become young froglets and start to venture onto land. They continue to grow and develop into adult frogs, capable of living both in water and on land. The life cycle comes full circle as adult frogs lay eggs and continue the cycle.
It’s essential to protect the habitats of frogs to ensure their survival. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change are significant threats to frog populations worldwide. By understanding and appreciating the life cycle of frogs, we can work towards conserving these unique and valuable amphibians.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a remarkable journey of transformation and adaptation. By learning about and respecting these creatures, we can contribute to their conservation and the preservation of their natural habitats. Let’s continue to explore and protect the diverse life forms that share our planet.