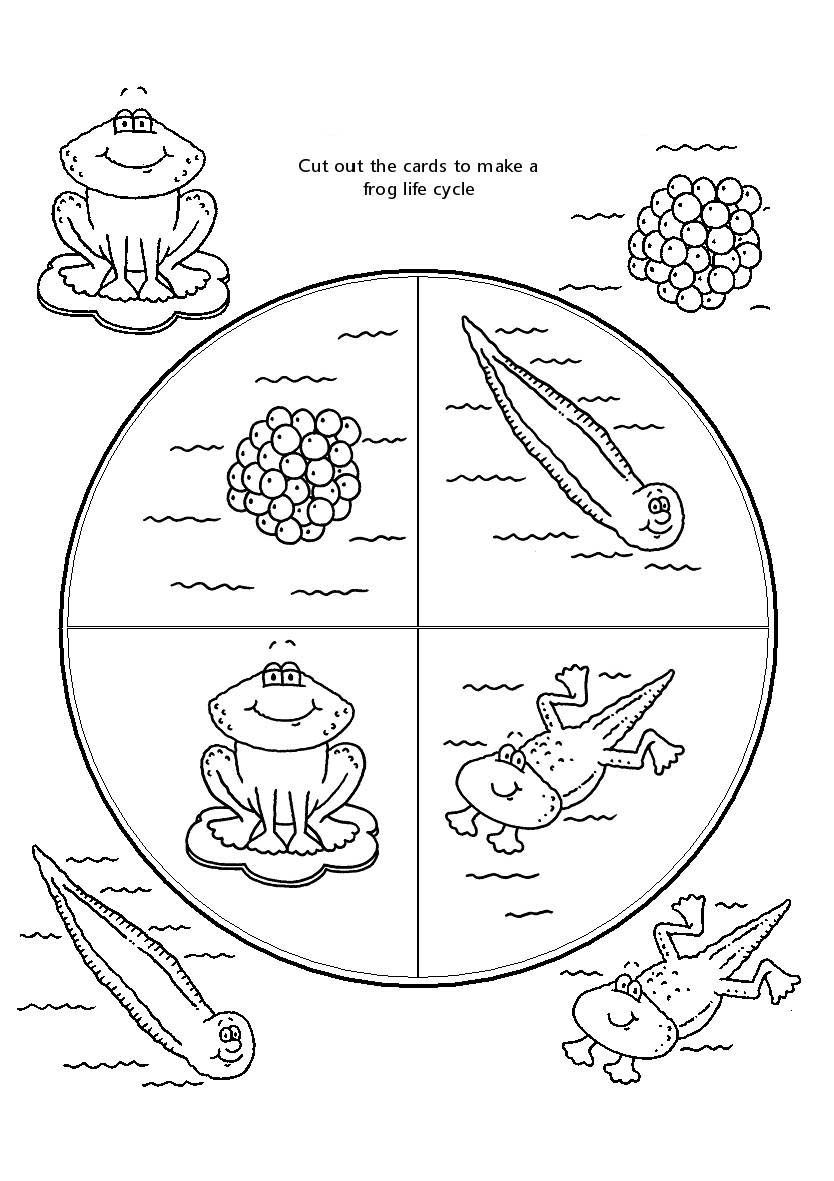
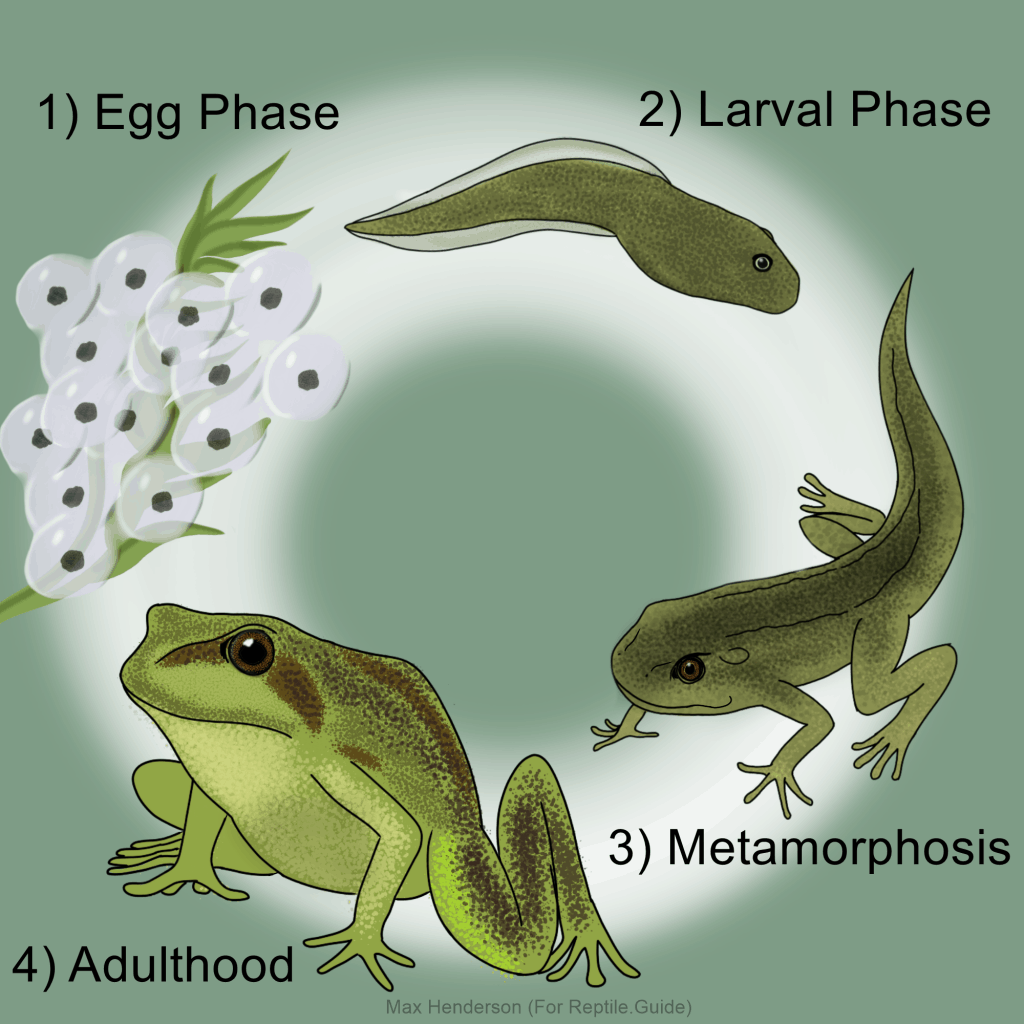
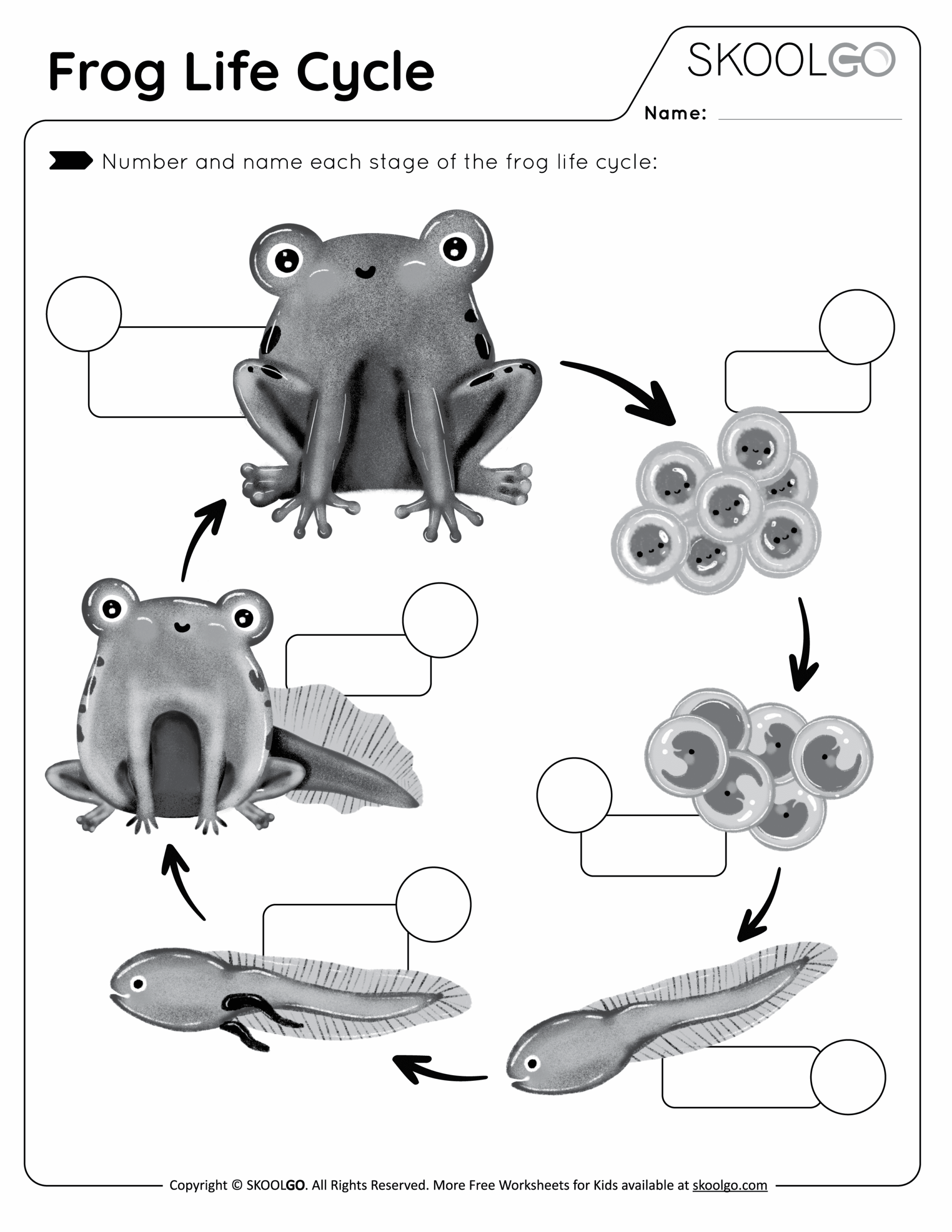
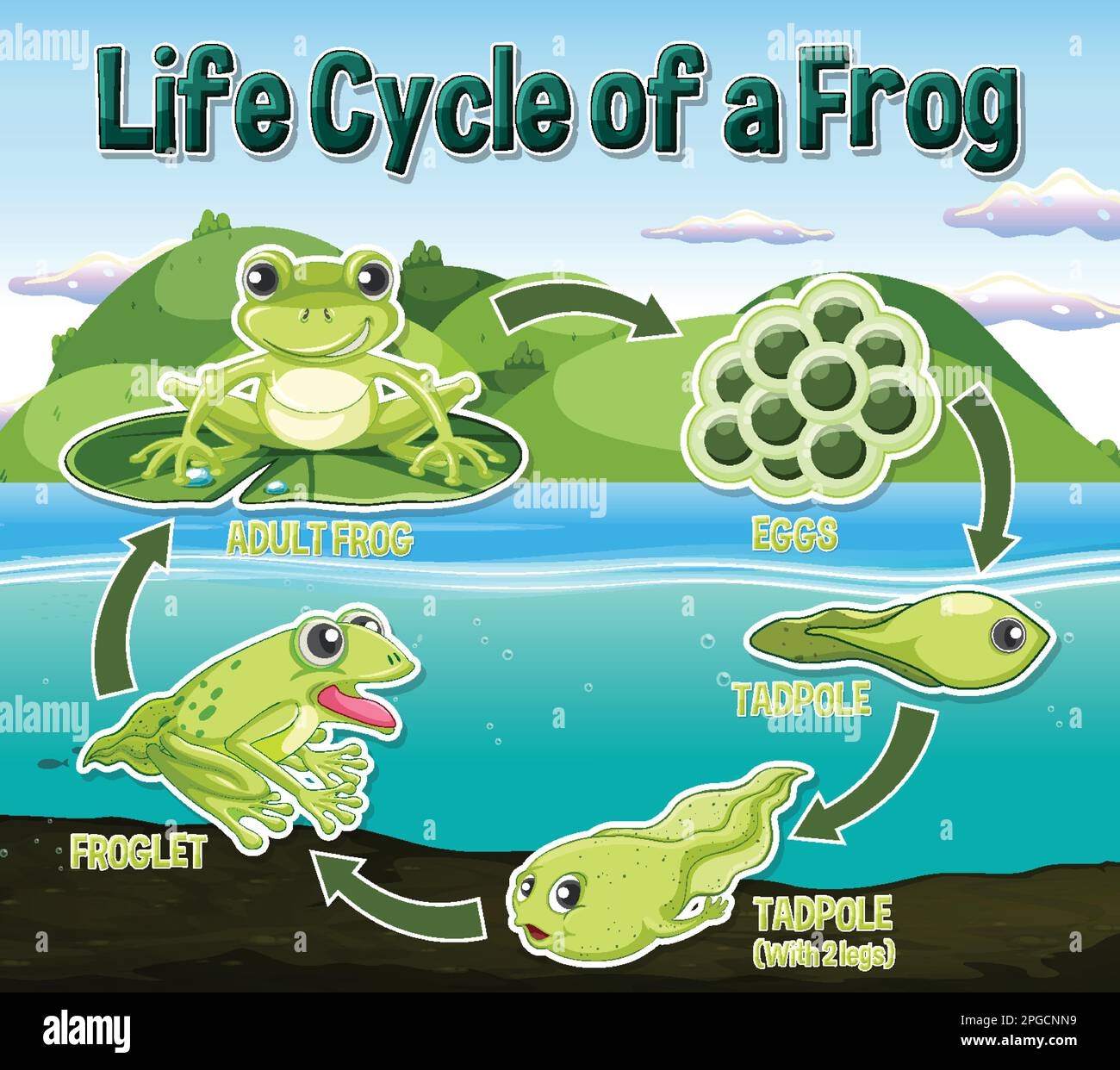
If you’ve ever wondered about the fascinating life cycle of a frog, you’re in for a treat. Frogs go through a unique transformation from egg to tadpole to adult frog that is both intriguing and important to their survival in the wild.
From the moment a frog lays its eggs in the water, the cycle of life begins. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which are aquatic and breathe through gills. As they grow, tadpoles develop legs and lungs, eventually transforming into adult frogs that live both on land and in the water.
Cycle Life of a Frog
One of the most interesting aspects of a frog’s life cycle is their ability to undergo metamorphosis. This process involves a series of physical changes that allow them to adapt to different environments as they mature. From swimming as tadpoles to hopping as adult frogs, each stage serves a unique purpose in their development.
As adult frogs, these amphibians play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They eat insects, control pest populations, and serve as a food source for other animals. Their presence in wetlands and water bodies is a sign of a healthy environment, making them essential to the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem.
Unfortunately, frogs face numerous threats in the wild, including habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these fascinating creatures and ensure their survival for future generations to enjoy. By learning more about the cycle of life of a frog, we can better appreciate the importance of preserving their habitats and supporting their conservation.
In conclusion, the cycle of life of a frog is a remarkable journey that highlights the interconnectedness of all living things in nature. By understanding and respecting these creatures, we can help protect their habitats and ensure their continued existence for years to come.