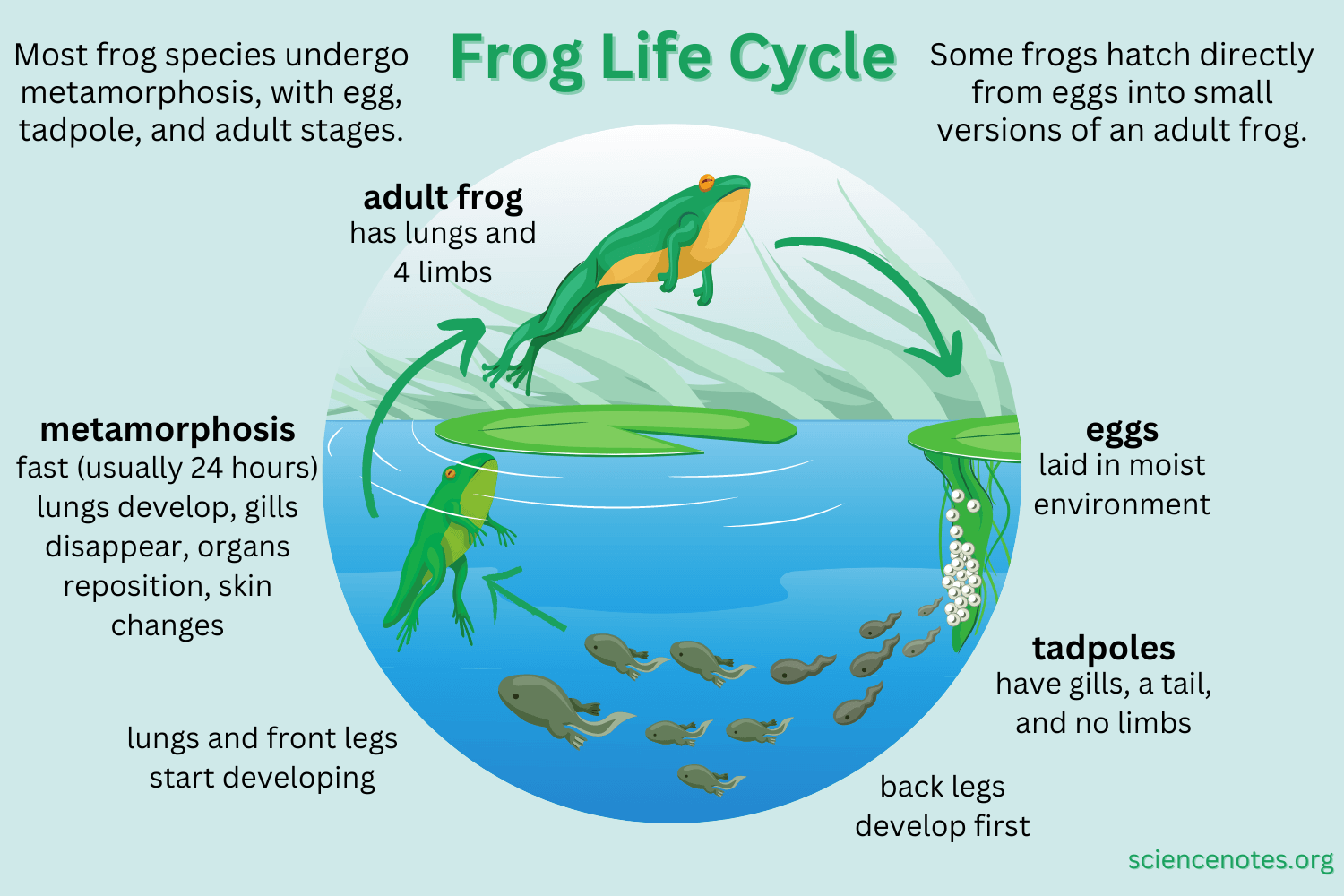
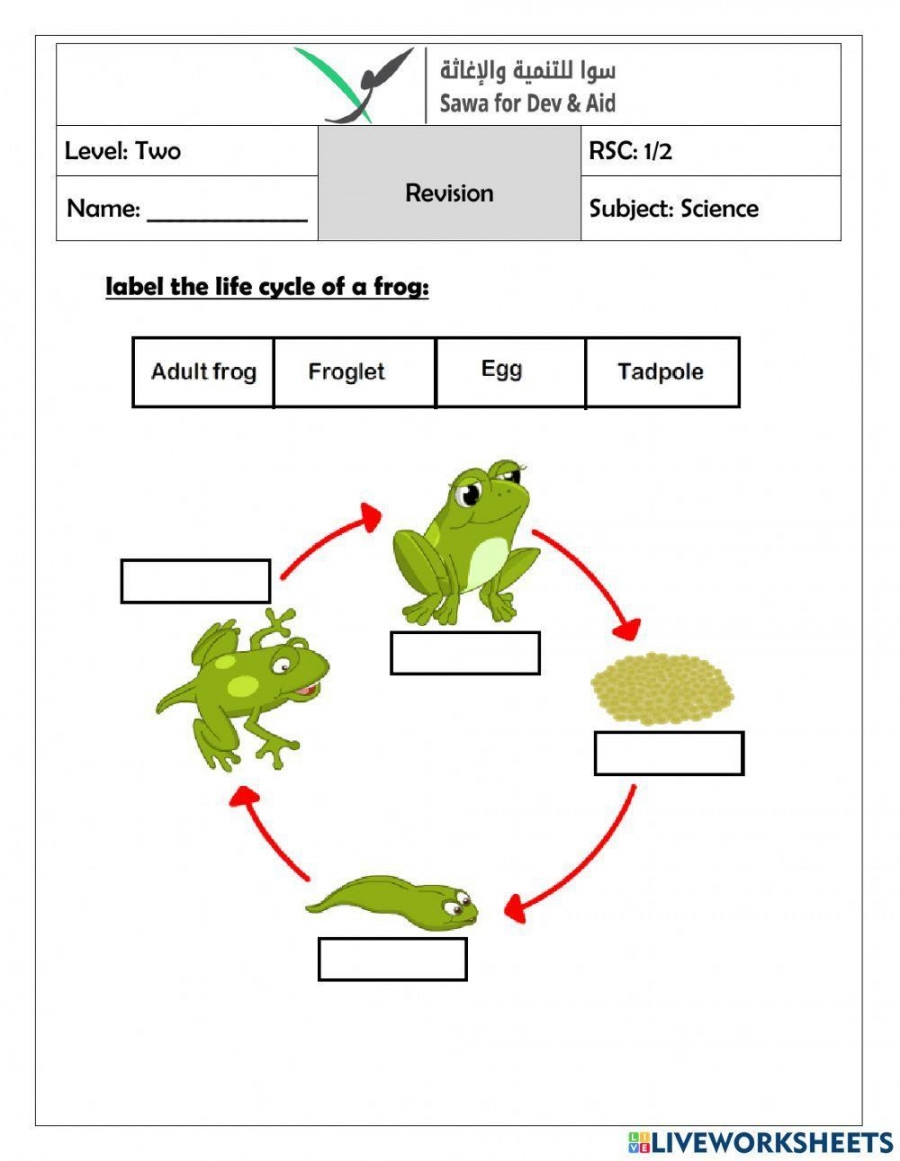
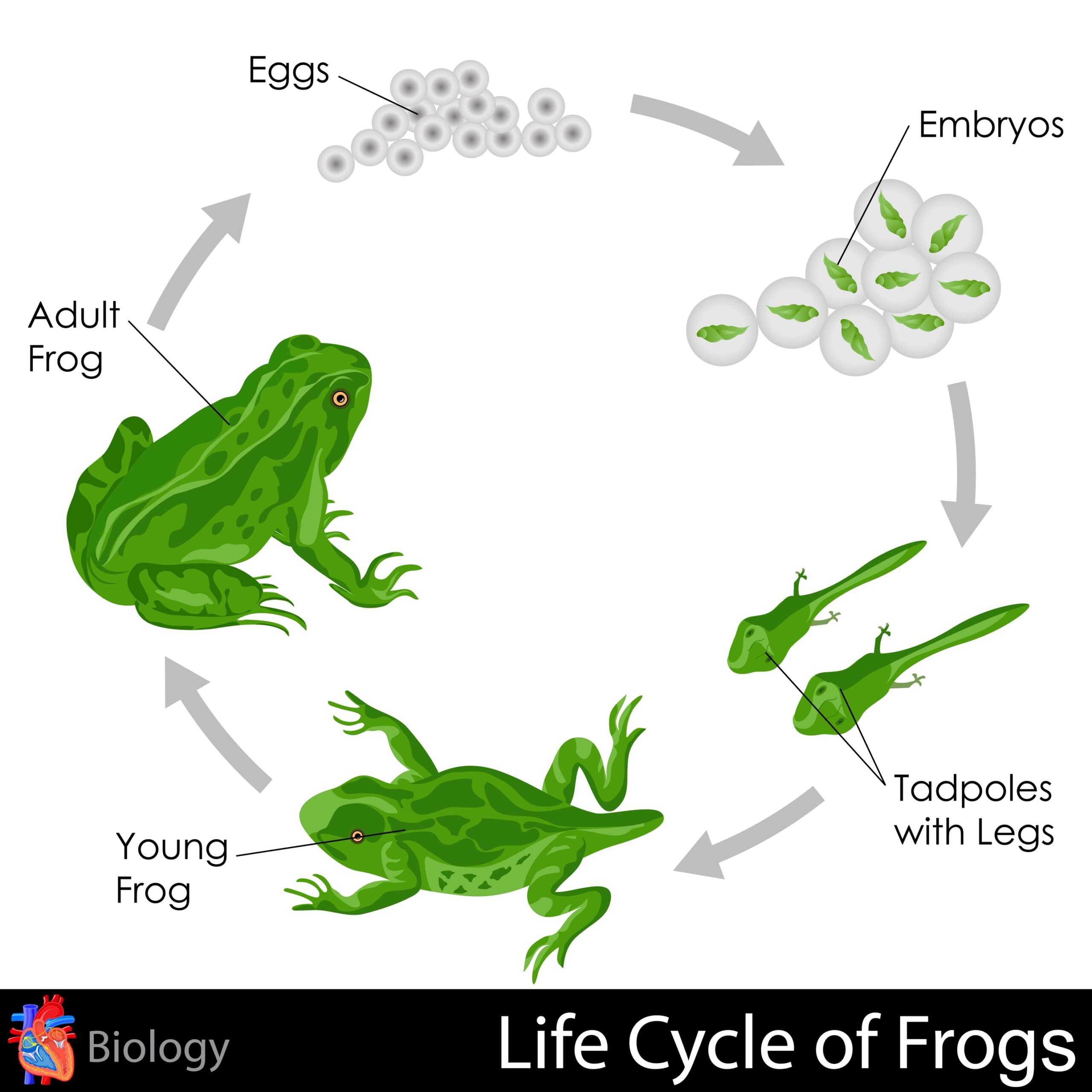
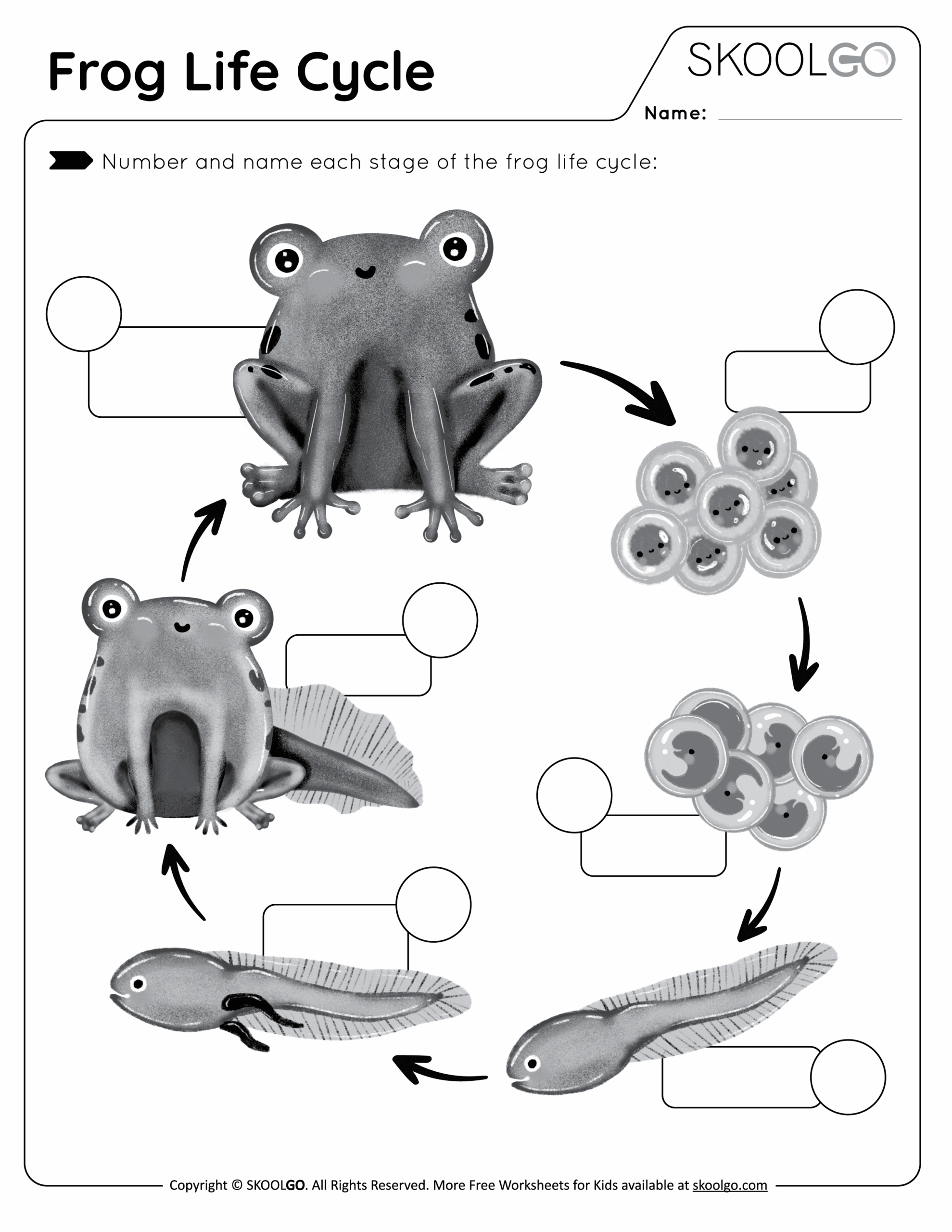
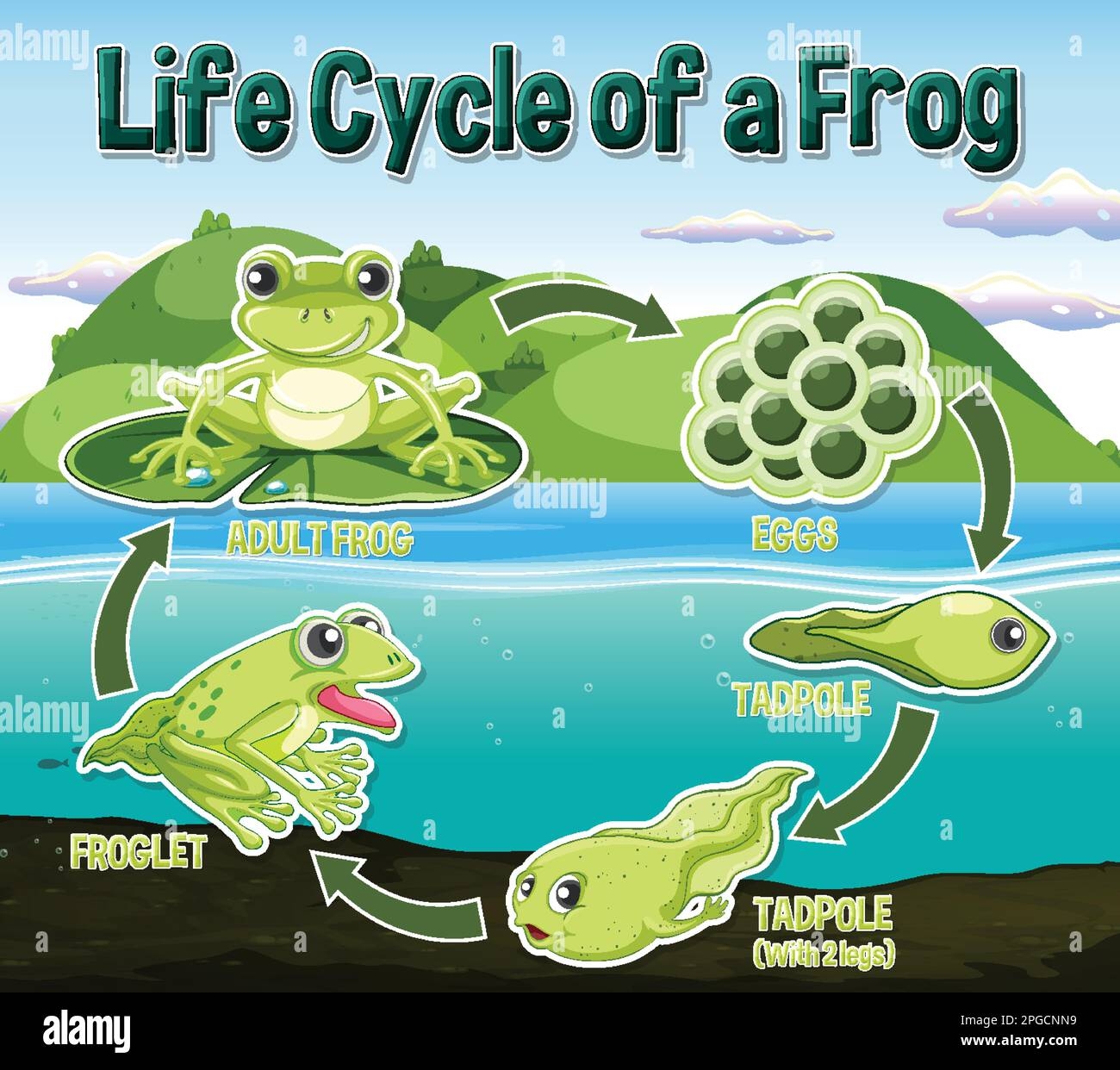
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through a unique life cycle, starting as tiny eggs and transforming into hopping amphibians. Understanding the cycle of a frog’s life can provide valuable insight into the natural world and the interconnectedness of ecosystems.
The cycle of a frog’s life begins with the female frog laying eggs in water, typically in a pond or stream. These eggs are enclosed in a jelly-like substance to protect them from predators. Over time, the eggs hatch into tadpoles, which have gills for breathing underwater.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo a remarkable transformation known as metamorphosis. During this process, tadpoles develop legs, absorb their tails, and develop lungs for breathing air. This transformation allows them to leave the water and live on land as adult frogs.
Once they have completed metamorphosis, adult frogs will spend their days hunting insects and other small prey. They are essential members of their ecosystems, helping to control insect populations and serving as a food source for larger animals.
Frogs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the natural world, making their life cycle an essential part of the ecosystem. By studying the cycle of a frog’s life, scientists can better understand the interconnectedness of all living things.
In conclusion, the cycle of a frog’s life is a remarkable journey that showcases the wonders of nature. From tiny eggs to hopping amphibians, frogs go through a fascinating transformation that highlights the beauty and complexity of the natural world. Take the time to observe these amazing creatures in their natural habitats and appreciate the role they play in our ecosystems.