Have you ever wondered about the fascinating life cycle of a frog? These amphibians go through some incredible transformations as they grow from eggs to adults.
From tadpoles to full-grown frogs, each stage of their life cycle is truly remarkable. Let’s dive into the process and understand how frogs develop over time.
Explaining the Life Cycle of a Frog
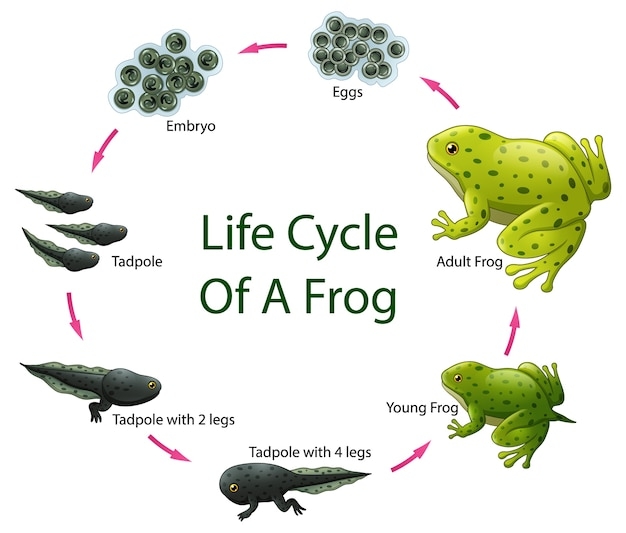
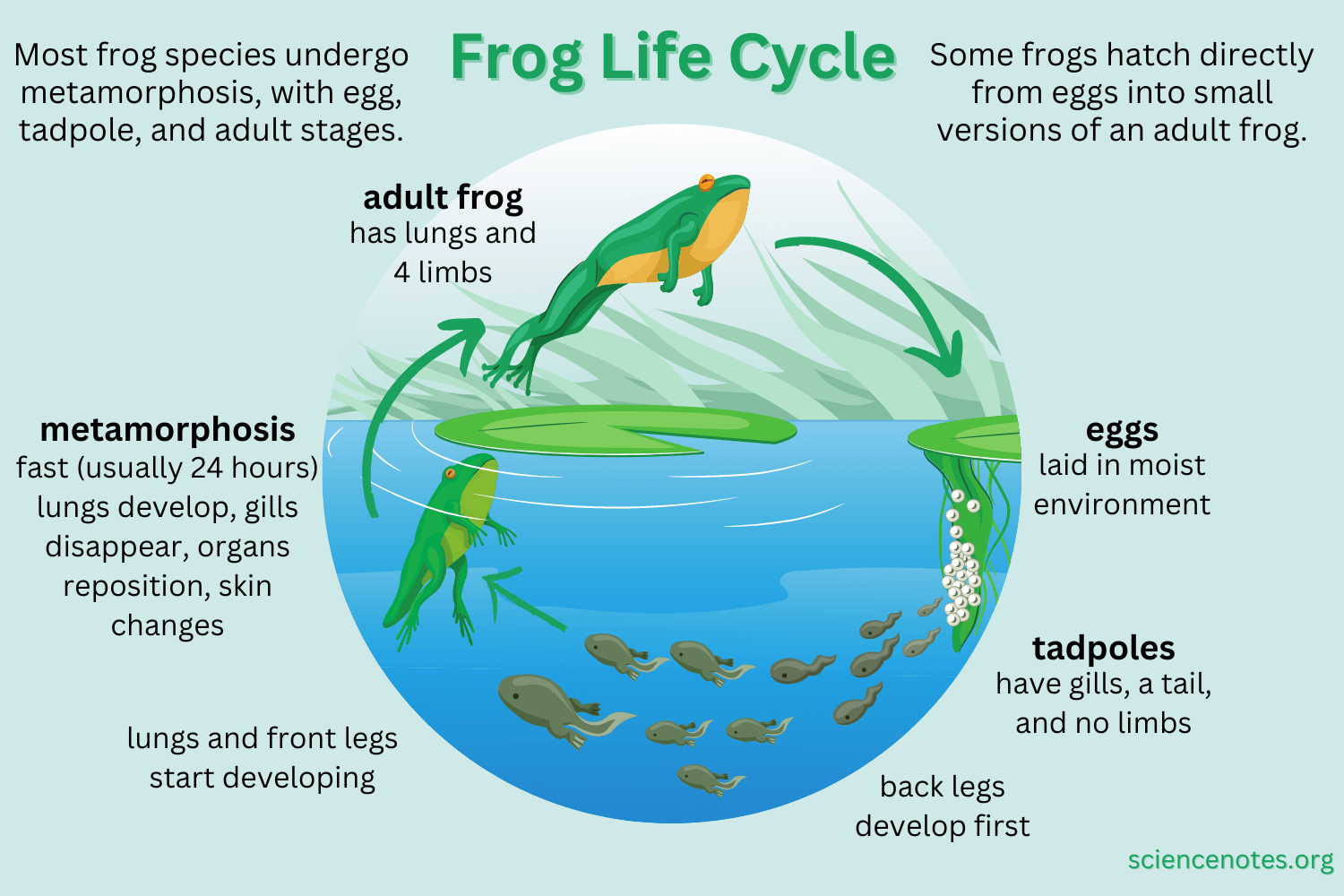
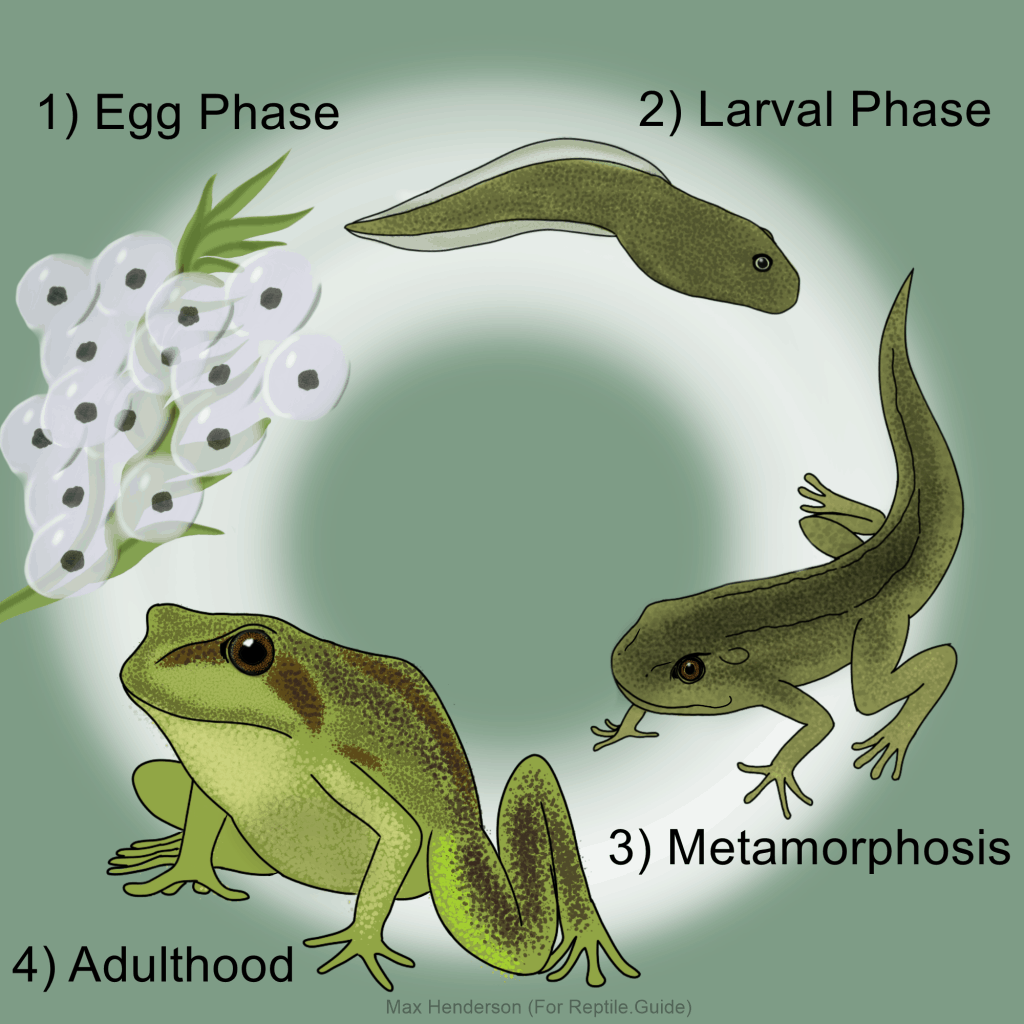
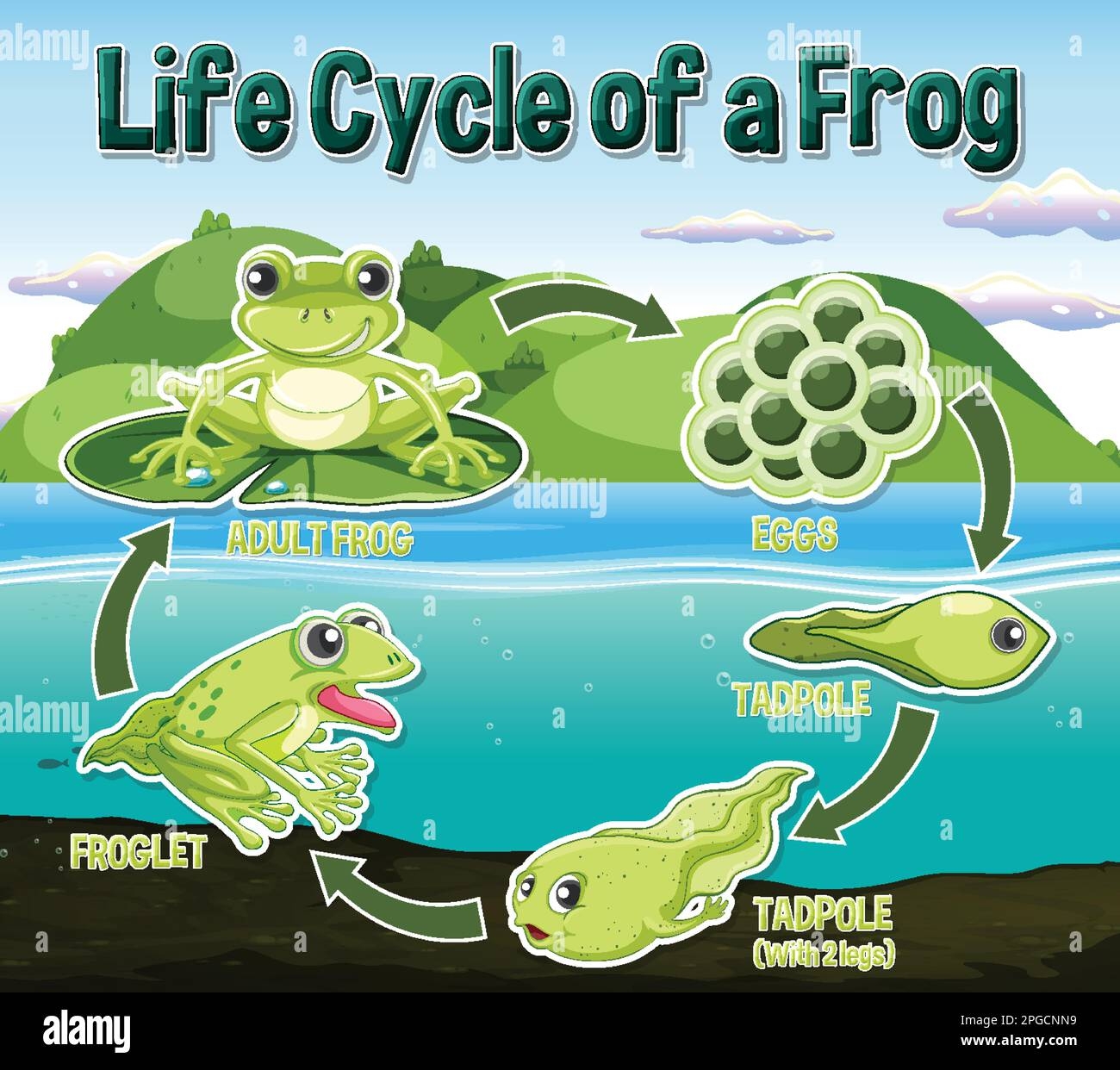
The life cycle of a frog begins with eggs. Female frogs lay eggs in water, which hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles have gills and tails, resembling fish more than frogs.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo metamorphosis. Their tails shrink, and legs begin to form. Lungs develop, allowing them to breathe air instead of relying on gills.
Once the transformation is complete, tadpoles turn into froglets. These young frogs have both lungs and a functional set of legs. They start to explore land while still living near water.
Finally, the froglets mature into adult frogs. They lose their tails and become fully adapted to life on land. Adult frogs can now reproduce and continue the cycle by laying eggs in water.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a fascinating journey of growth and transformation. From tiny eggs to hopping adults, these amphibians undergo incredible changes to survive and thrive in their environment.