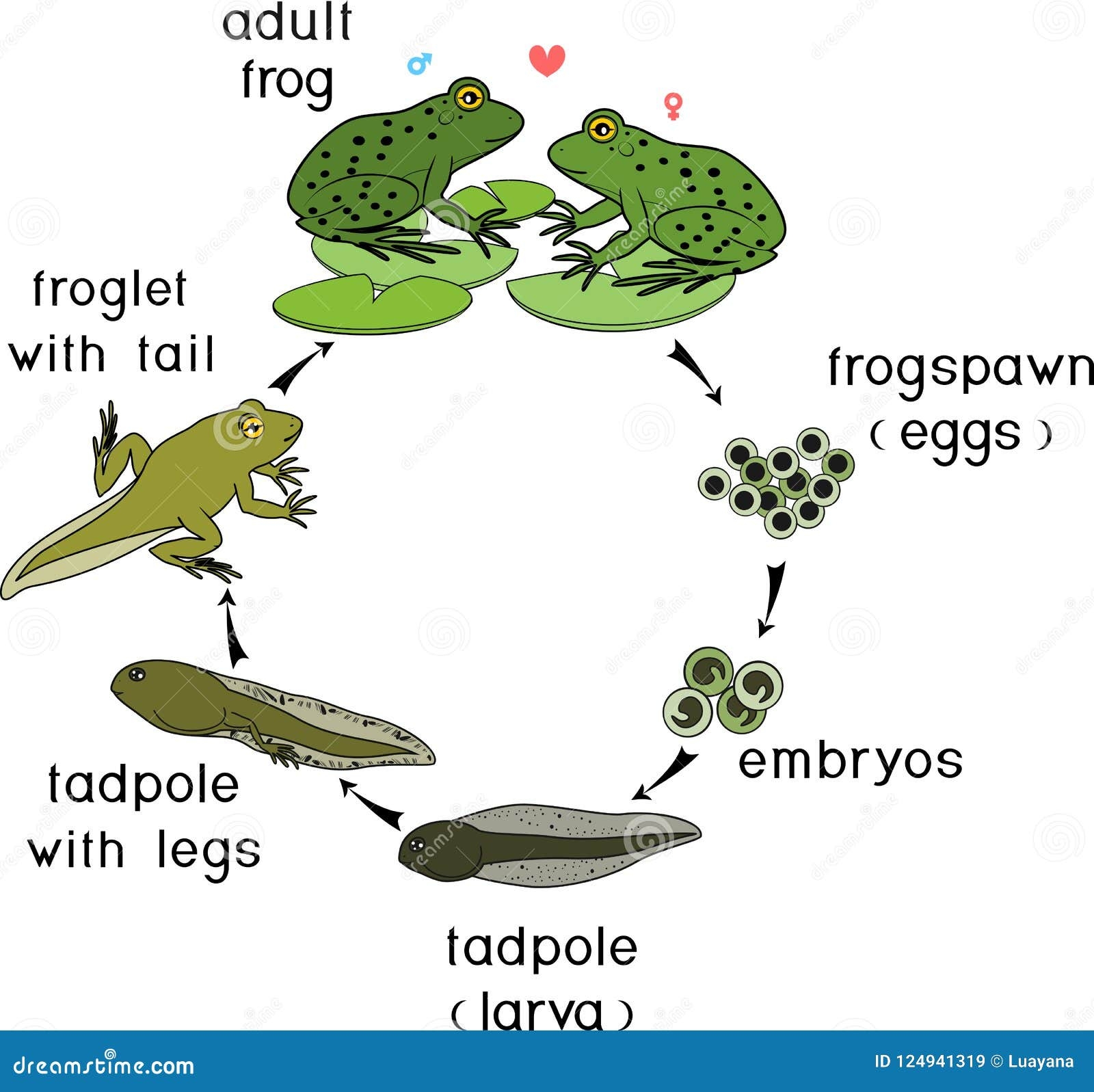
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through various stages in their life cycle. From tiny tadpoles to hopping adults, the transformation is truly incredible to witness. In this article, we will explore the different stages of a frog’s life cycle in detail.
Frog Life Cycle Stages
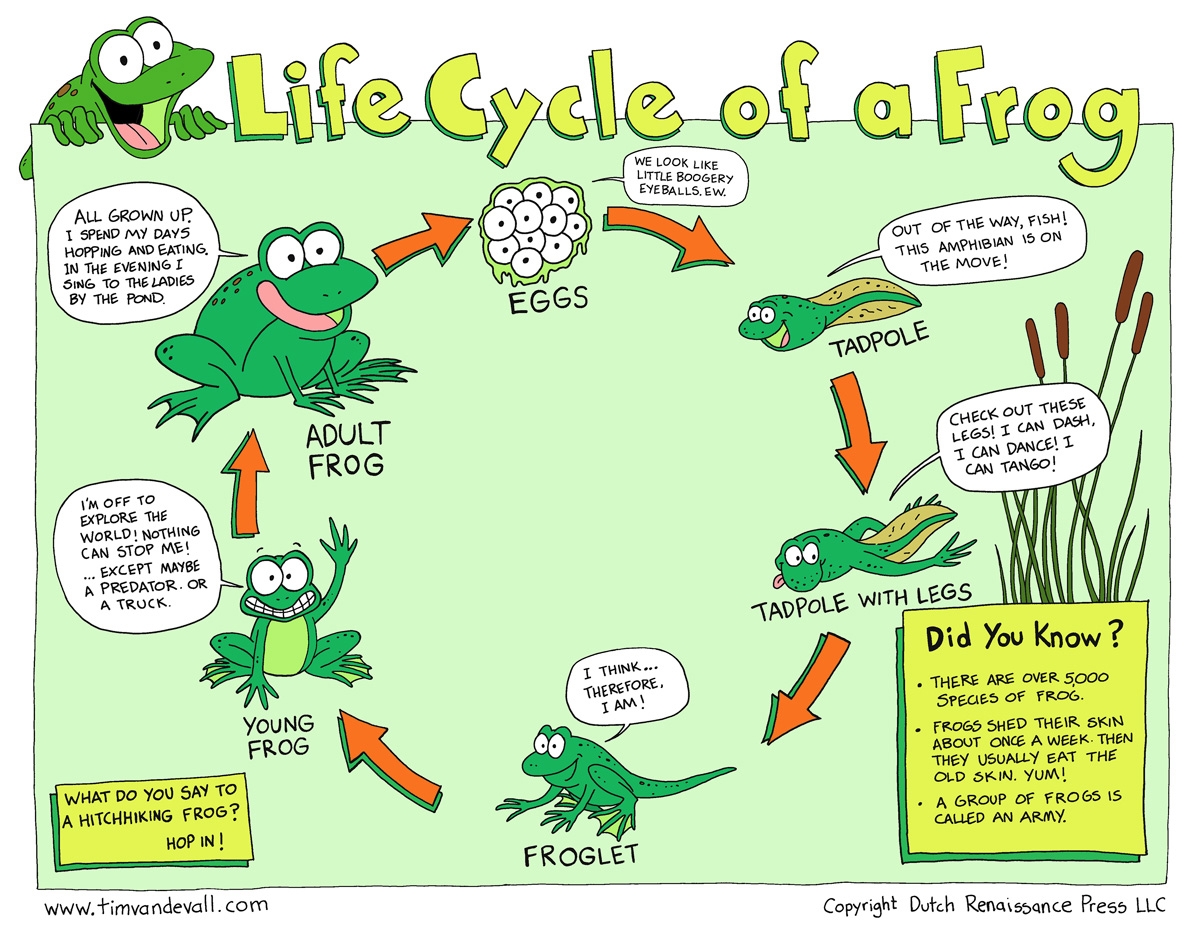
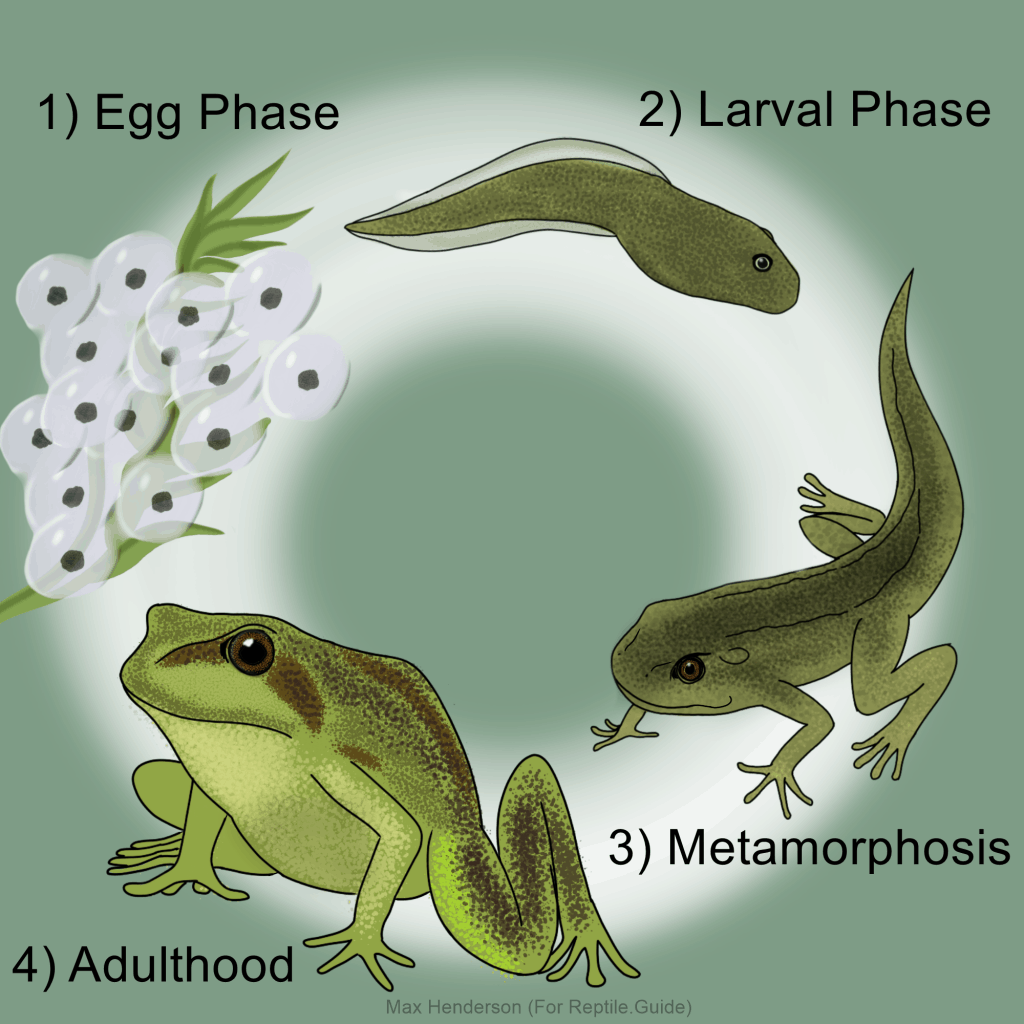
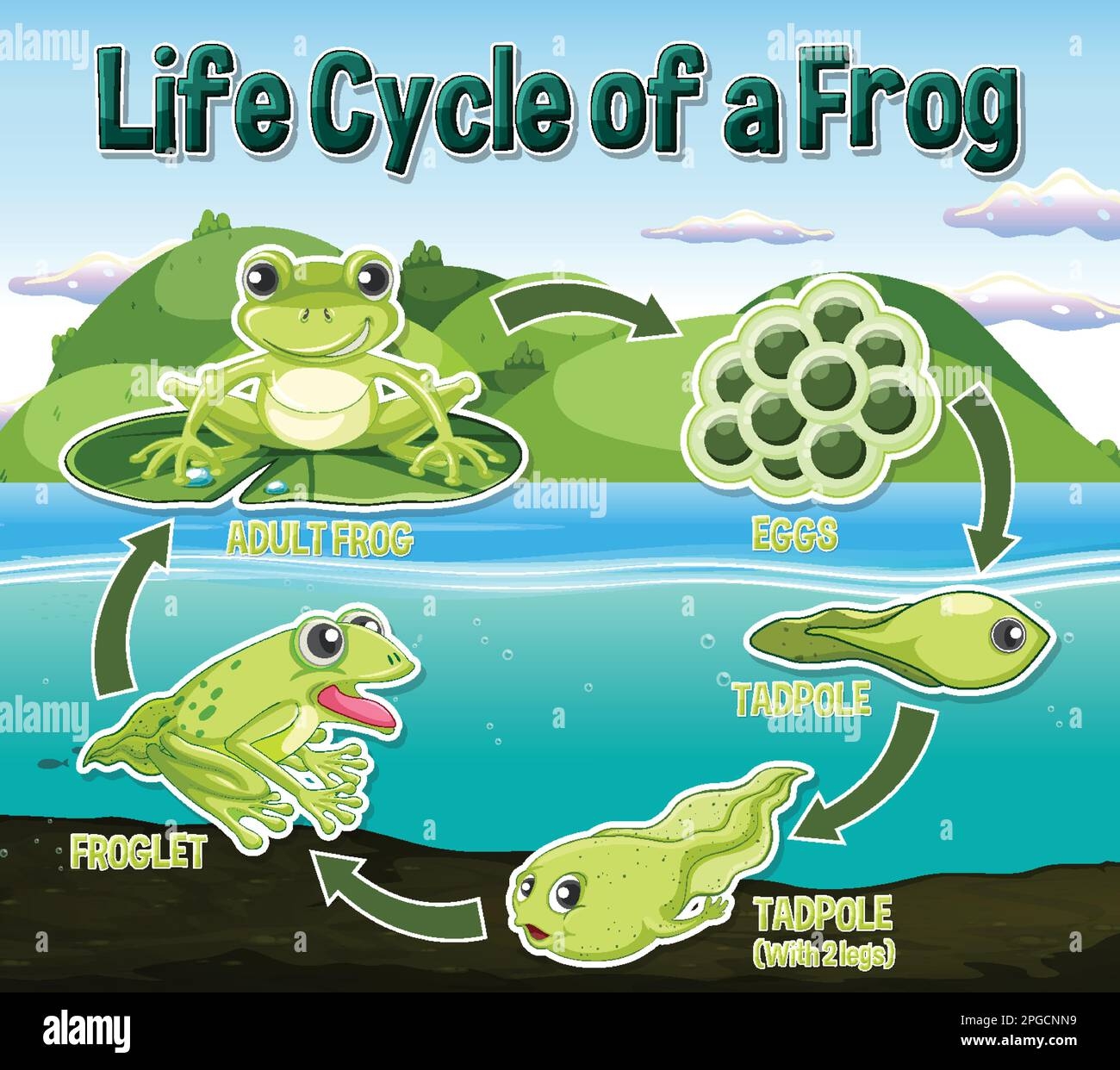
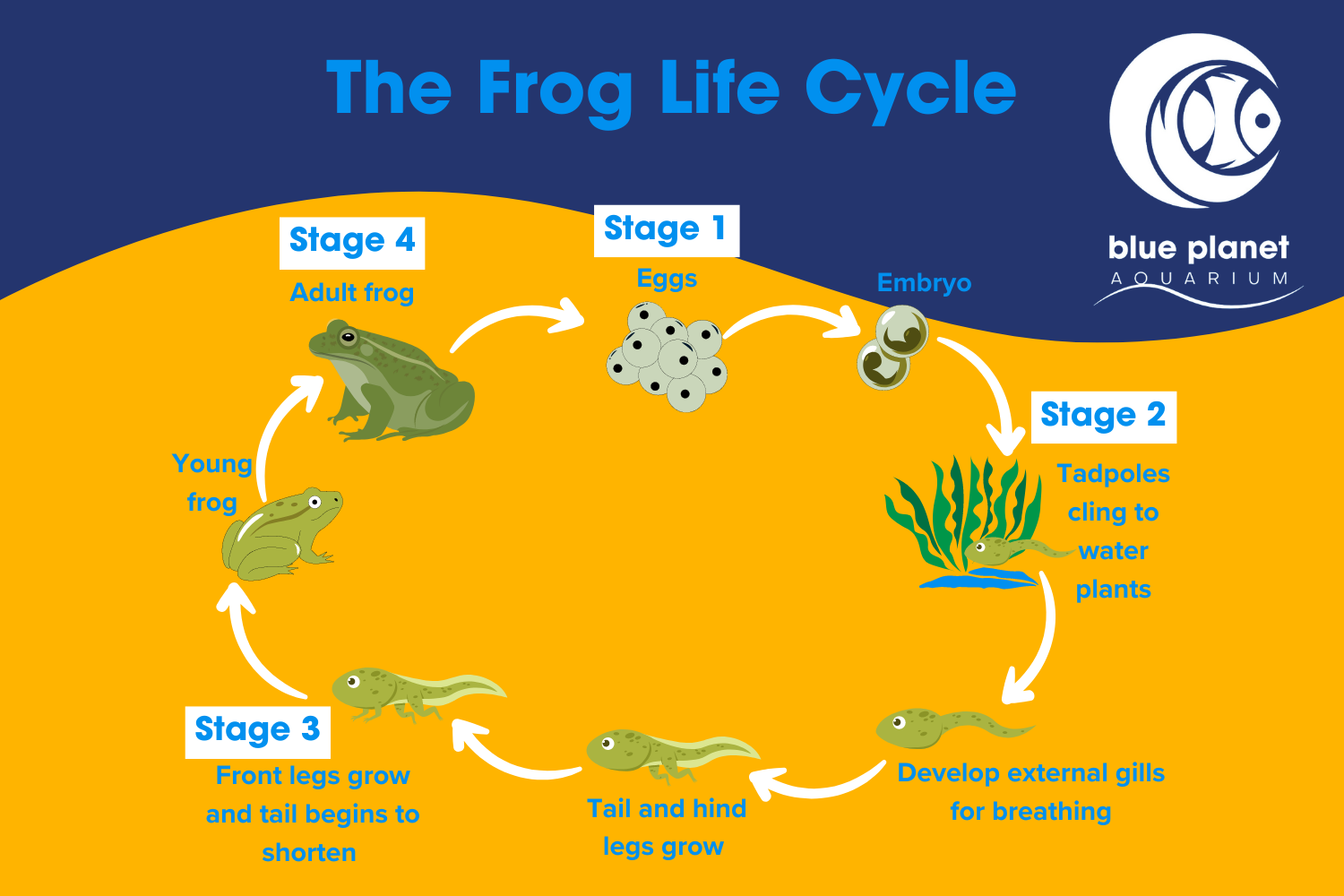
The first stage of a frog’s life cycle begins as an egg. Female frogs lay their eggs in water, often in large clusters. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which are aquatic larvae that breathe through gills and have tails for swimming.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo a process called metamorphosis. During this stage, they develop lungs for breathing air and lose their tails. Their legs start to grow, allowing them to eventually leave the water and become adult frogs.
Once the transformation is complete, the adult frog is ready to live on land. Frogs are known for their ability to jump long distances and catch insects with their sticky tongues. They also play a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and serving as food for other animals.
In some species, adult frogs return to the water to lay their own eggs, continuing the cycle. This cycle of egg, tadpole, metamorphosis, and adult frog repeats itself as the next generation of frogs is born and grows.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a remarkable journey that showcases the wonders of nature. By understanding the stages that these amphibians go through, we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of the natural world. Next time you see a frog, take a moment to marvel at the incredible transformation it has undergone in its life cycle.