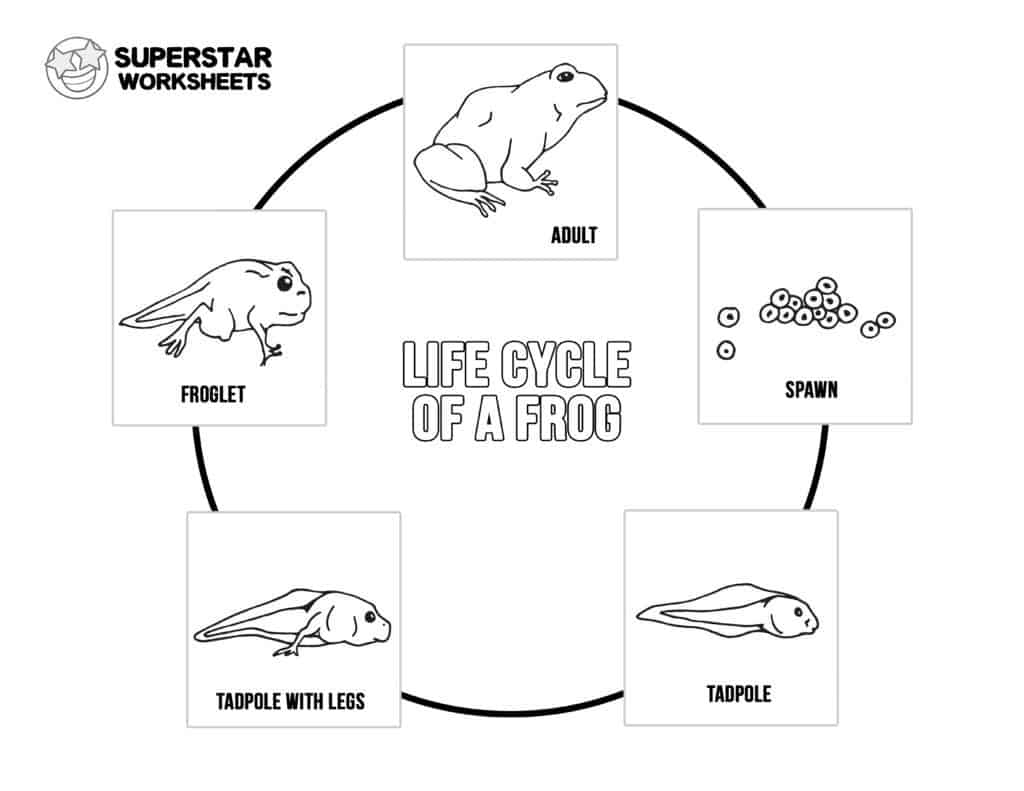
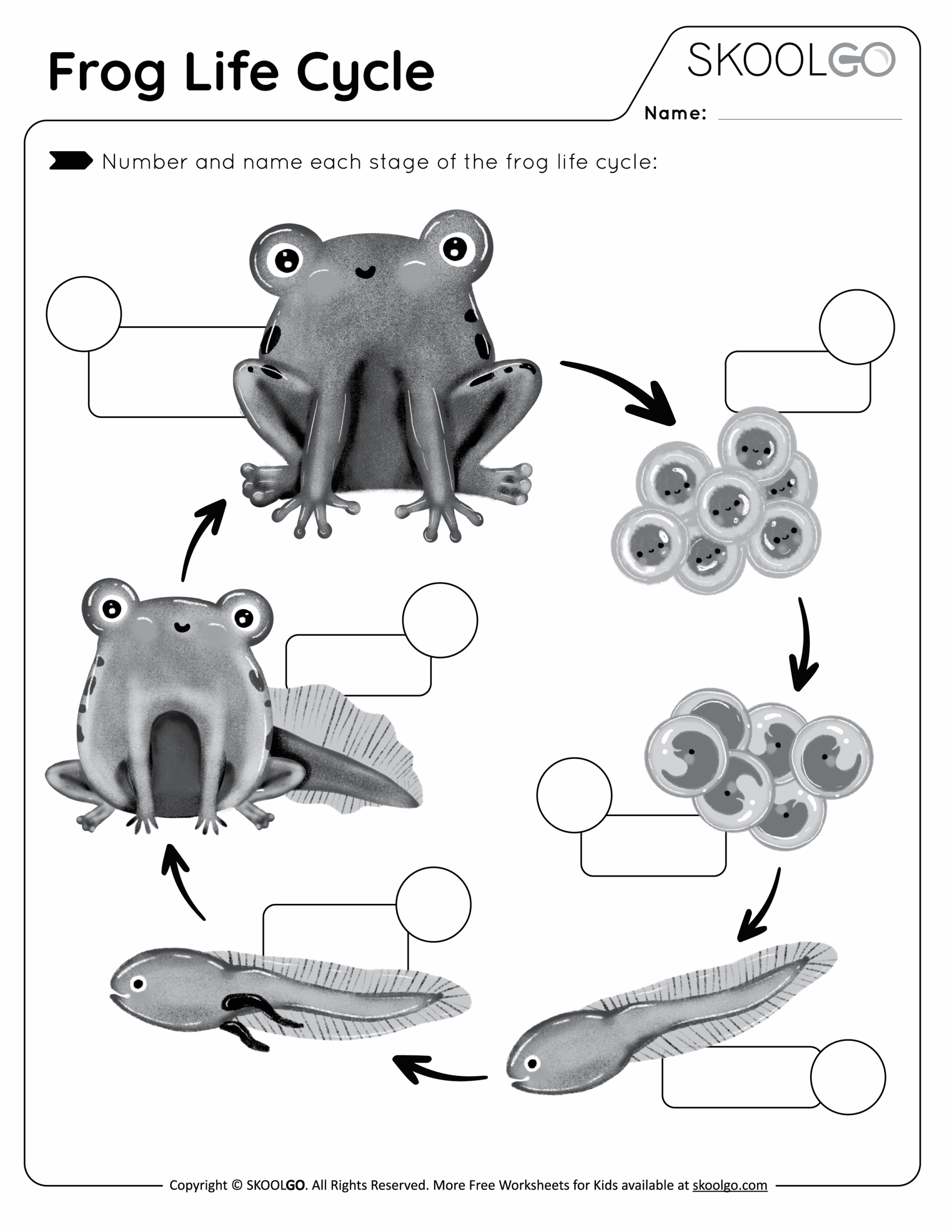
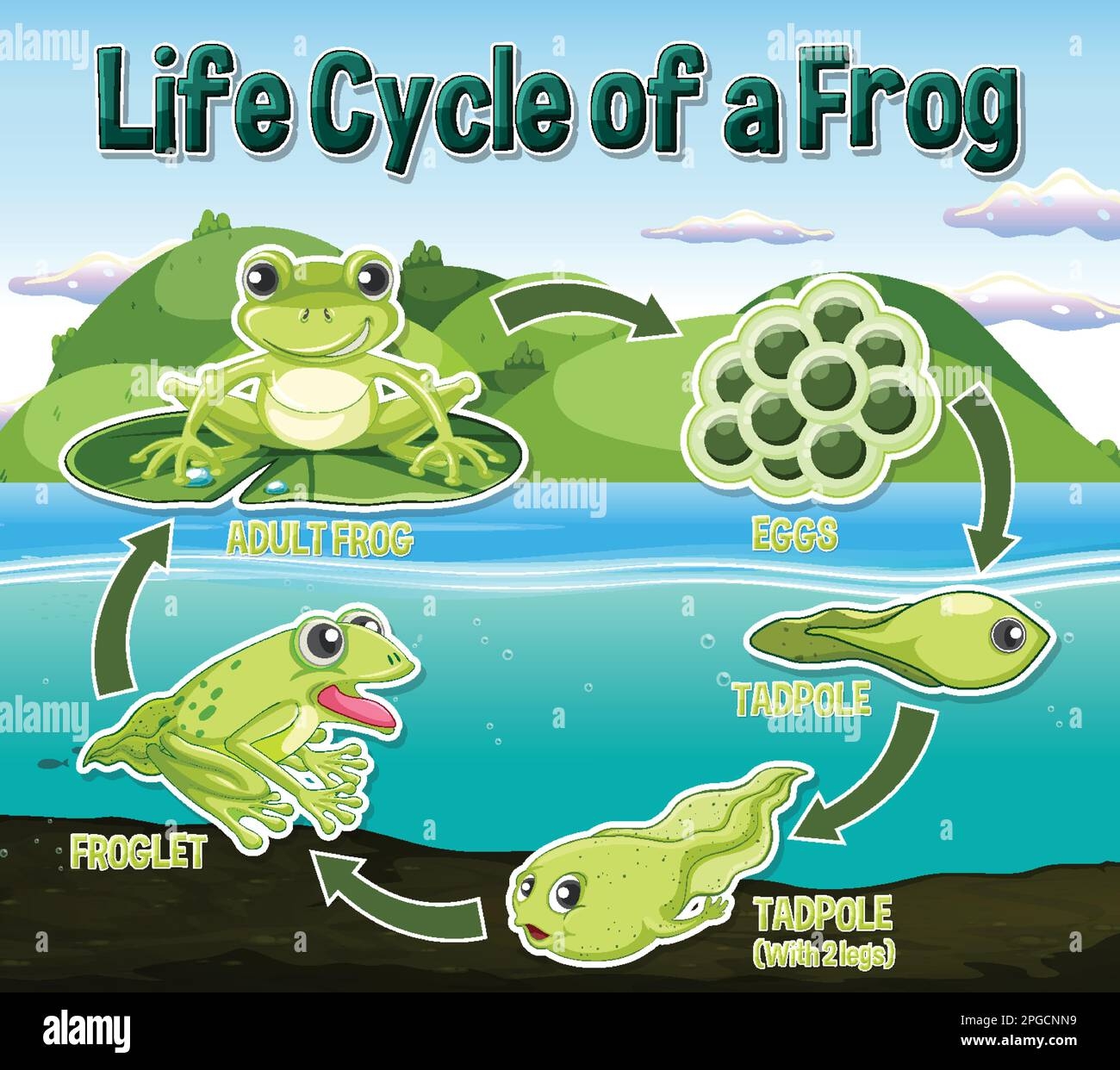
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through a unique life cycle. For kids, learning about the stages of a frog’s life can be both educational and entertaining. From eggs to tadpoles to adult frogs, each stage has its own characteristics and importance in the ecosystem.
The life cycle of a frog begins with the female frog laying eggs in water. These eggs are often laid in clusters and can be found attached to plants or floating on the surface of the water. The eggs hatch into tadpoles, which have gills for breathing underwater. Tadpoles feed on algae and other plants in the water.
As the tadpoles grow, they undergo metamorphosis, developing legs and lungs. They lose their tails and start to resemble adult frogs. This stage is known as the froglet stage. Finally, the froglet metamorphoses into an adult frog, leaving the water and starting a life on land. Adult frogs have lungs for breathing air and powerful hind legs for jumping.
The life cycle of a frog is an example of metamorphosis, a process in which an organism undergoes a drastic change in form and structure. This adaptation allows frogs to live in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. By going through different stages, frogs are able to survive and thrive in diverse habitats.
Learning about the life cycle of a frog can help kids understand the importance of adaptation and change in nature. It also teaches them about the interconnectedness of living organisms and the environment. By observing frogs in their natural habitat and studying their life cycle, kids can develop a greater appreciation for the natural world.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a fascinating journey that starts in water and ends on land. By learning about the stages of a frog’s life, kids can gain a deeper understanding of nature and the processes that shape living organisms. Next time you see a frog, take a moment to appreciate the incredible transformation it has undergone.