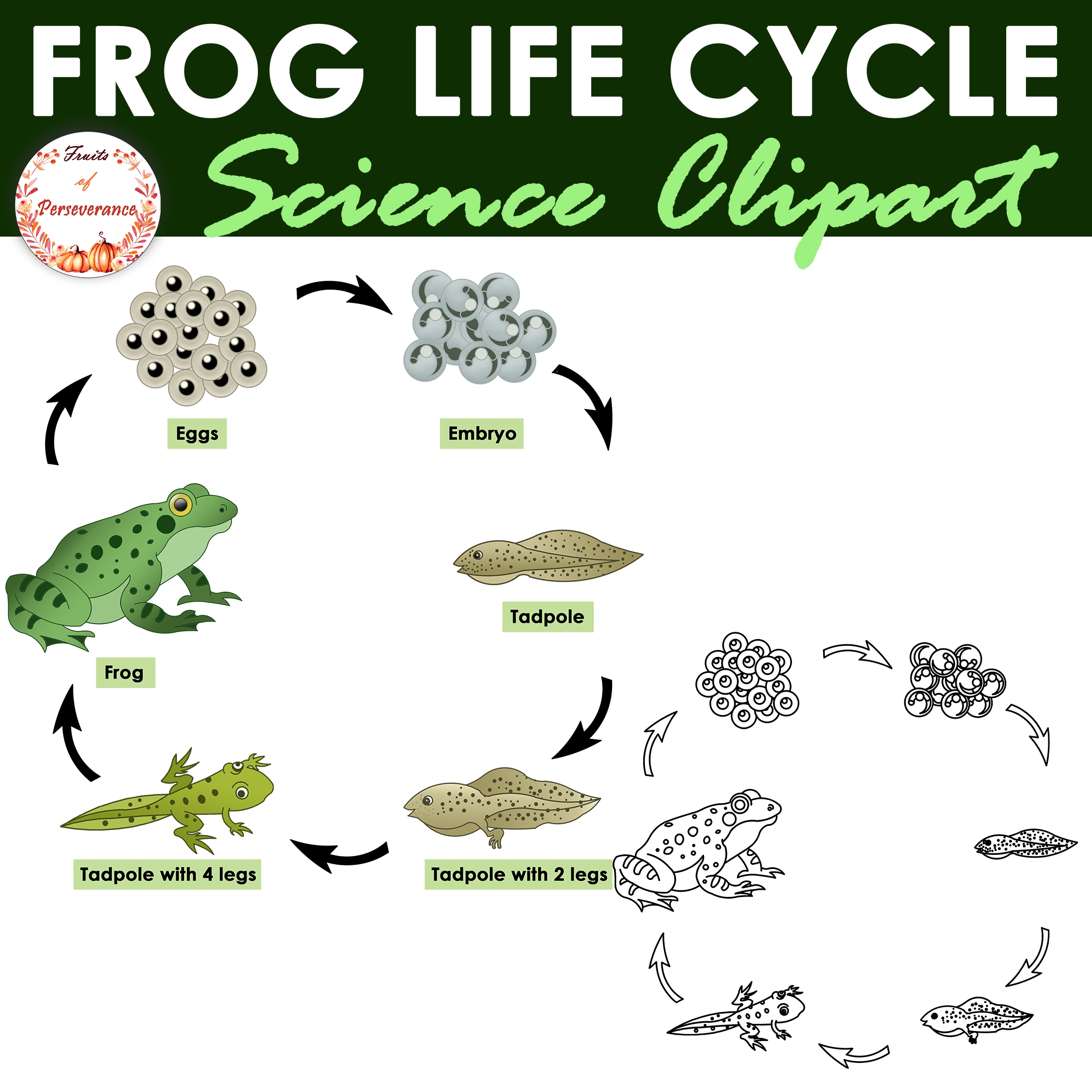
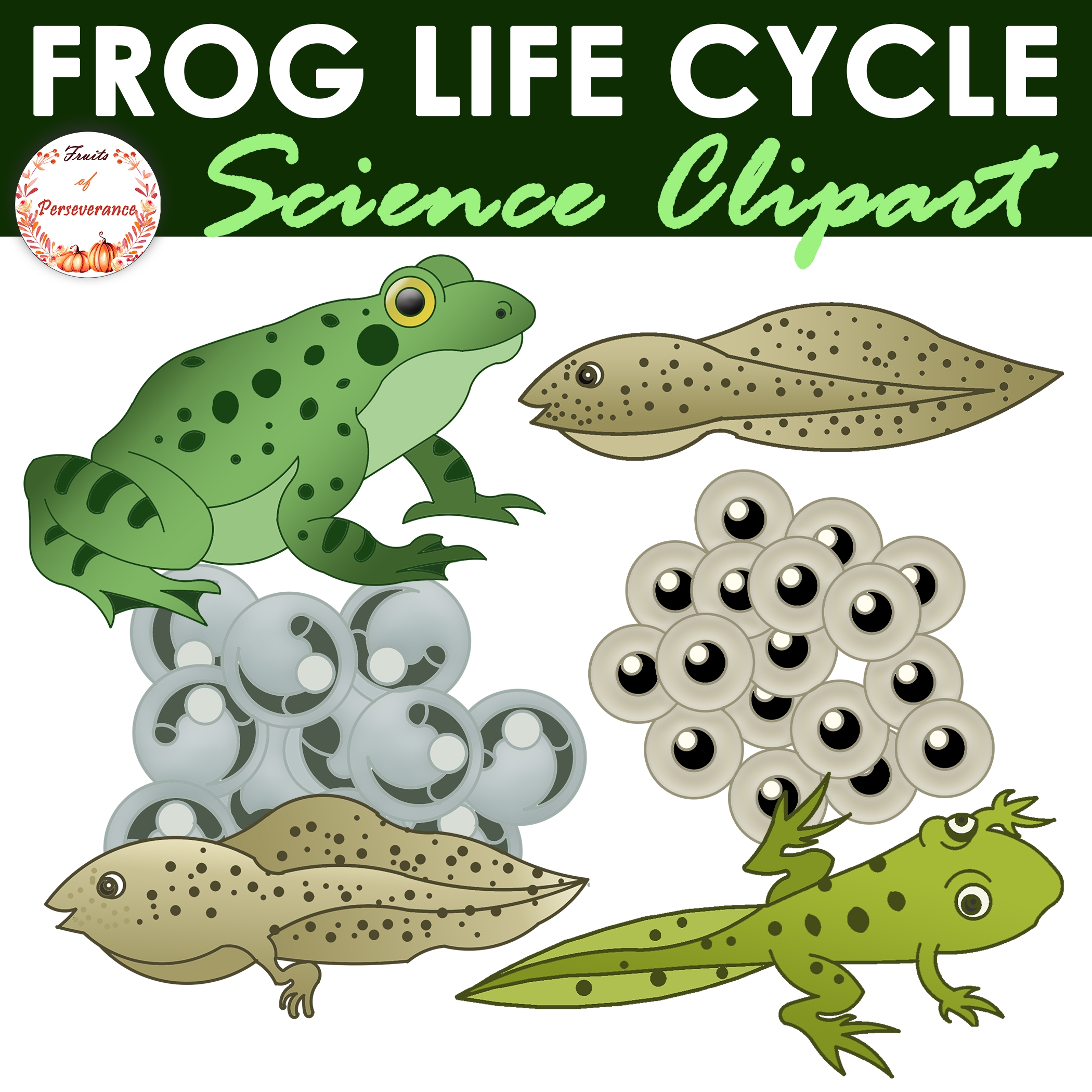
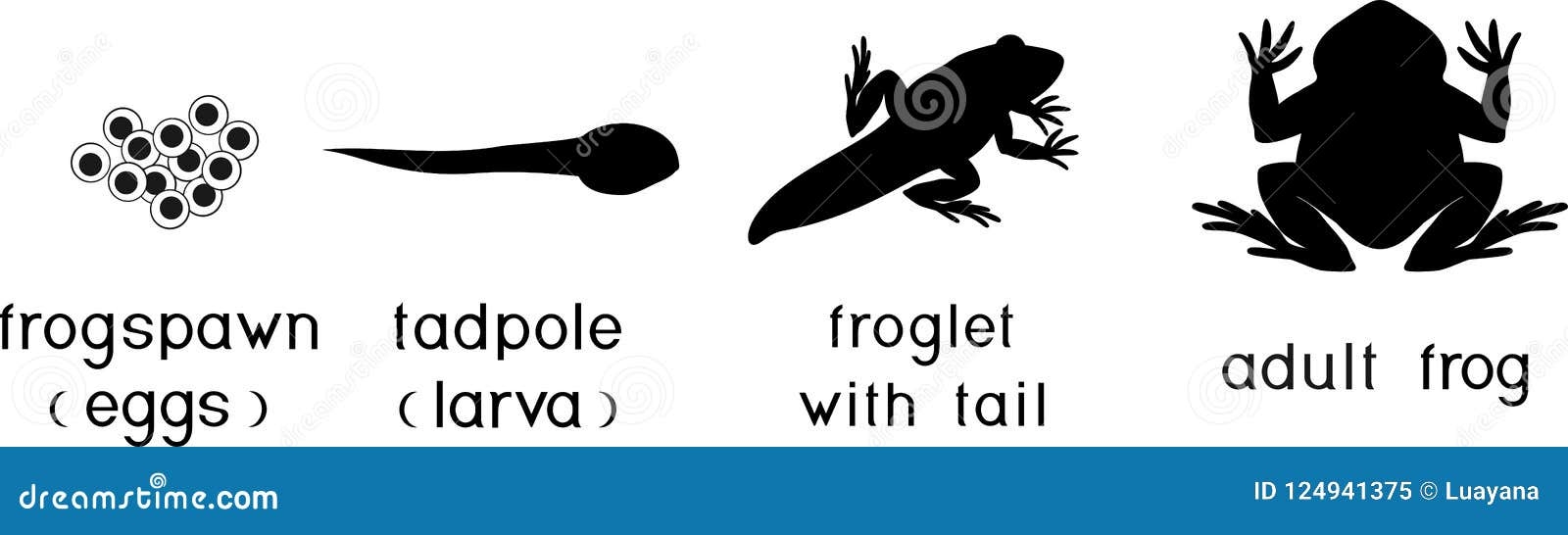
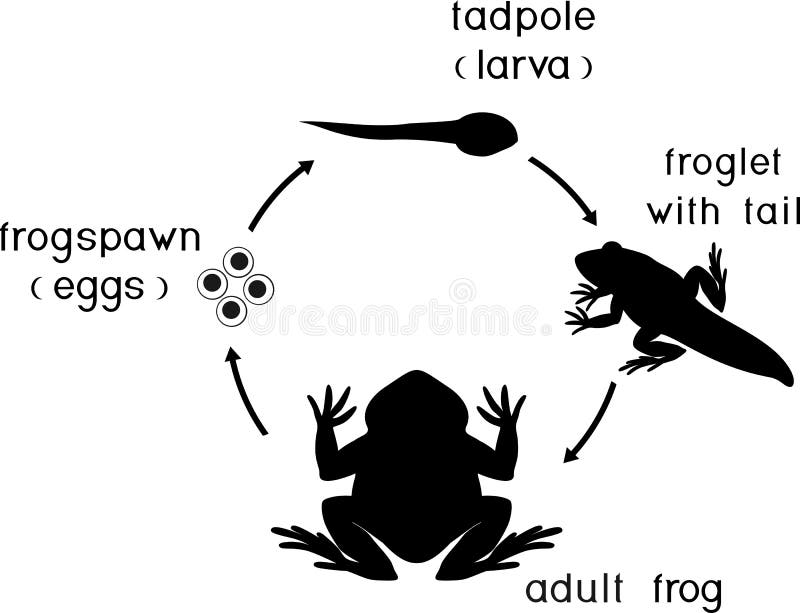
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through various stages of development before reaching adulthood. From tiny tadpoles to fully-formed frogs, the journey of a frog is truly remarkable. Understanding the stages of frog development can provide valuable insights into their life cycle and behavior.
During the first stage of frog development, eggs are laid in water by adult frogs. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which are aquatic larvae with gills for breathing underwater. Tadpoles feed on algae and small insects as they grow and develop.
As tadpoles grow, they undergo a metamorphosis process where they gradually lose their gills and develop lungs for breathing air. Their tails also shrink and eventually disappear as their legs begin to grow. This transformation is essential for tadpoles to adapt to life on land as adult frogs.
Once tadpoles complete their metamorphosis, they emerge from the water as young frogs. These juvenile frogs still have small tails and are not fully developed. Over time, they continue to grow and mature, shedding their tails and fully developing into adult frogs.
The final stage of frog development is when adult frogs reach sexual maturity and are able to reproduce. Male frogs develop vocal sacs to attract females through their unique calls, while females lay eggs for fertilization. This cyclical process continues as frogs reproduce and the life cycle repeats.
In conclusion, the stages of frog development are a fascinating journey that showcases the remarkable transformation these amphibians undergo from eggs to adults. By understanding the different stages of frog development, we can appreciate the complexity of their life cycle and the importance of conserving their habitats for future generations to enjoy.