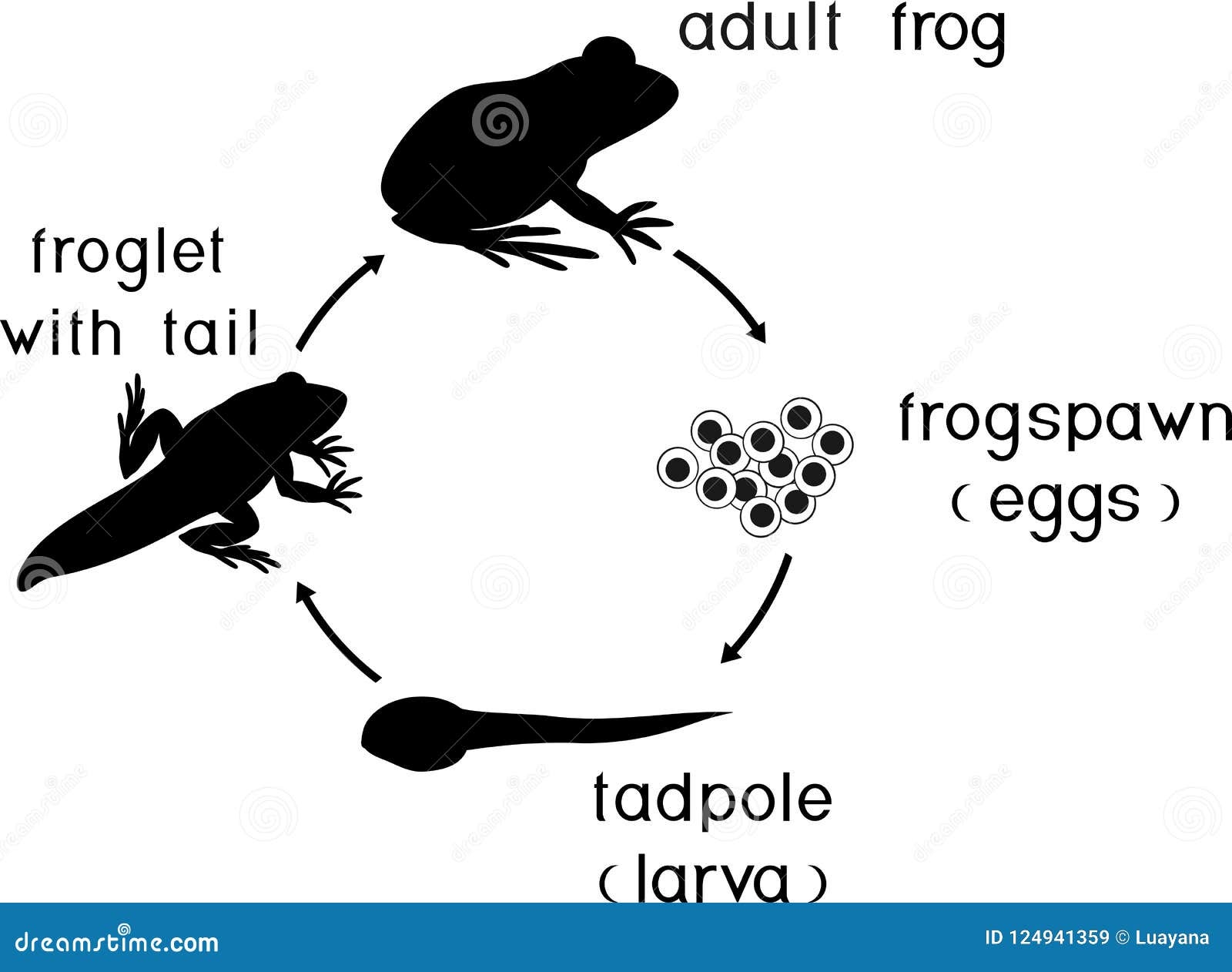
Frogs are fascinating creatures that go through a unique life cycle. From tiny tadpoles to hopping amphibians, the stages of a frog’s life are truly remarkable. Let’s dive into the different phases that make up the life cycle of a frog.
Stages of the Life Cycle of a Frog
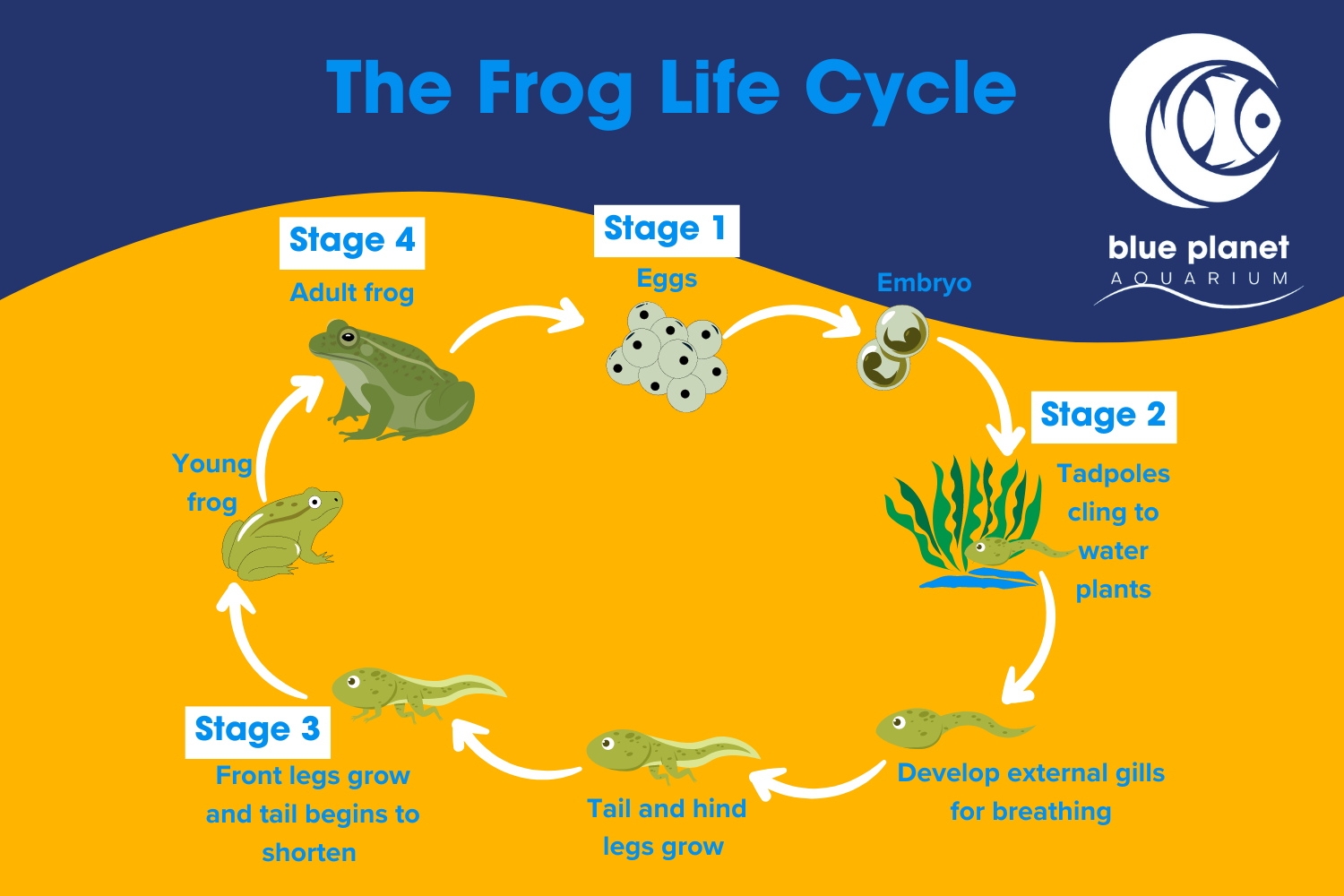
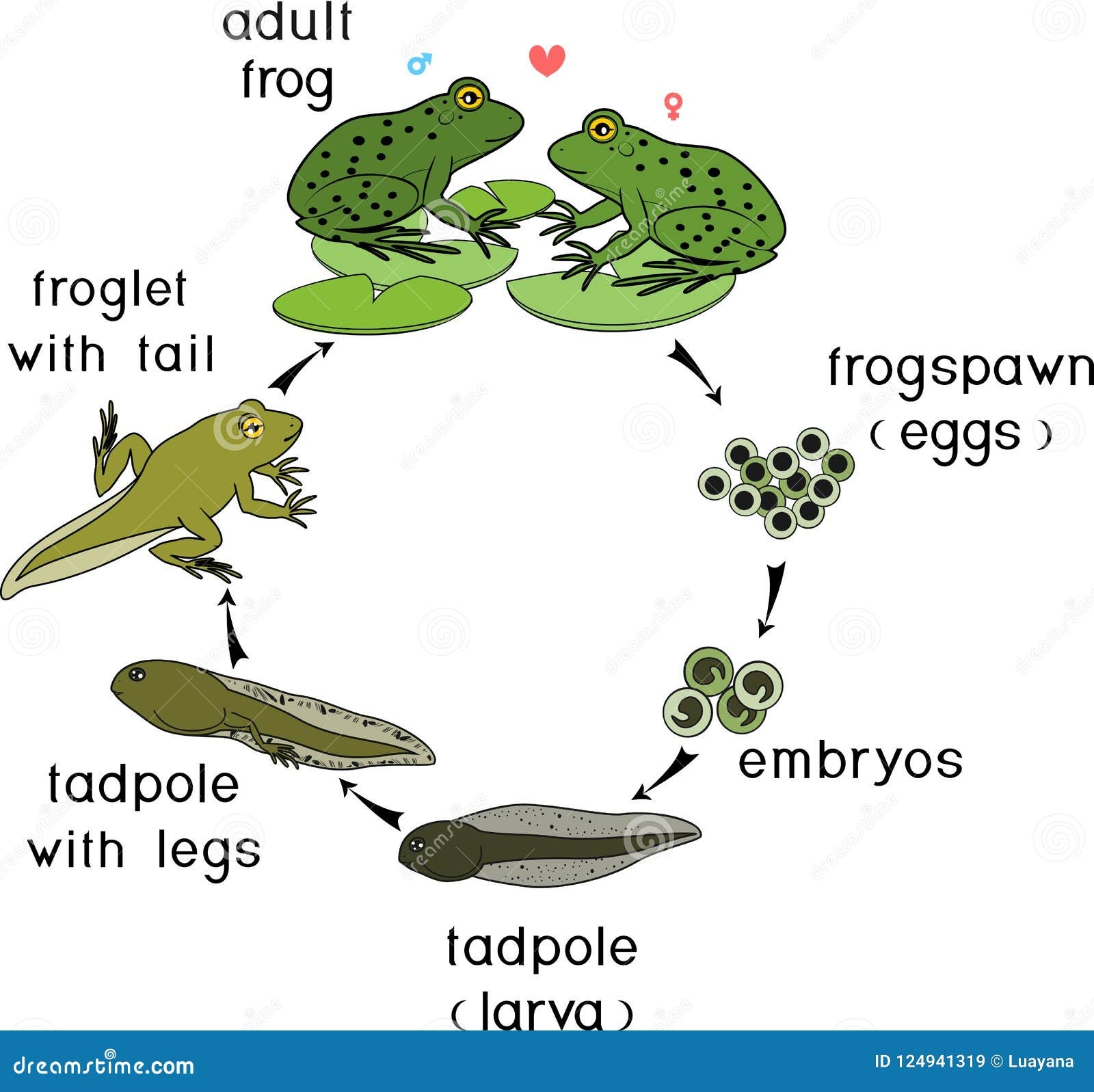
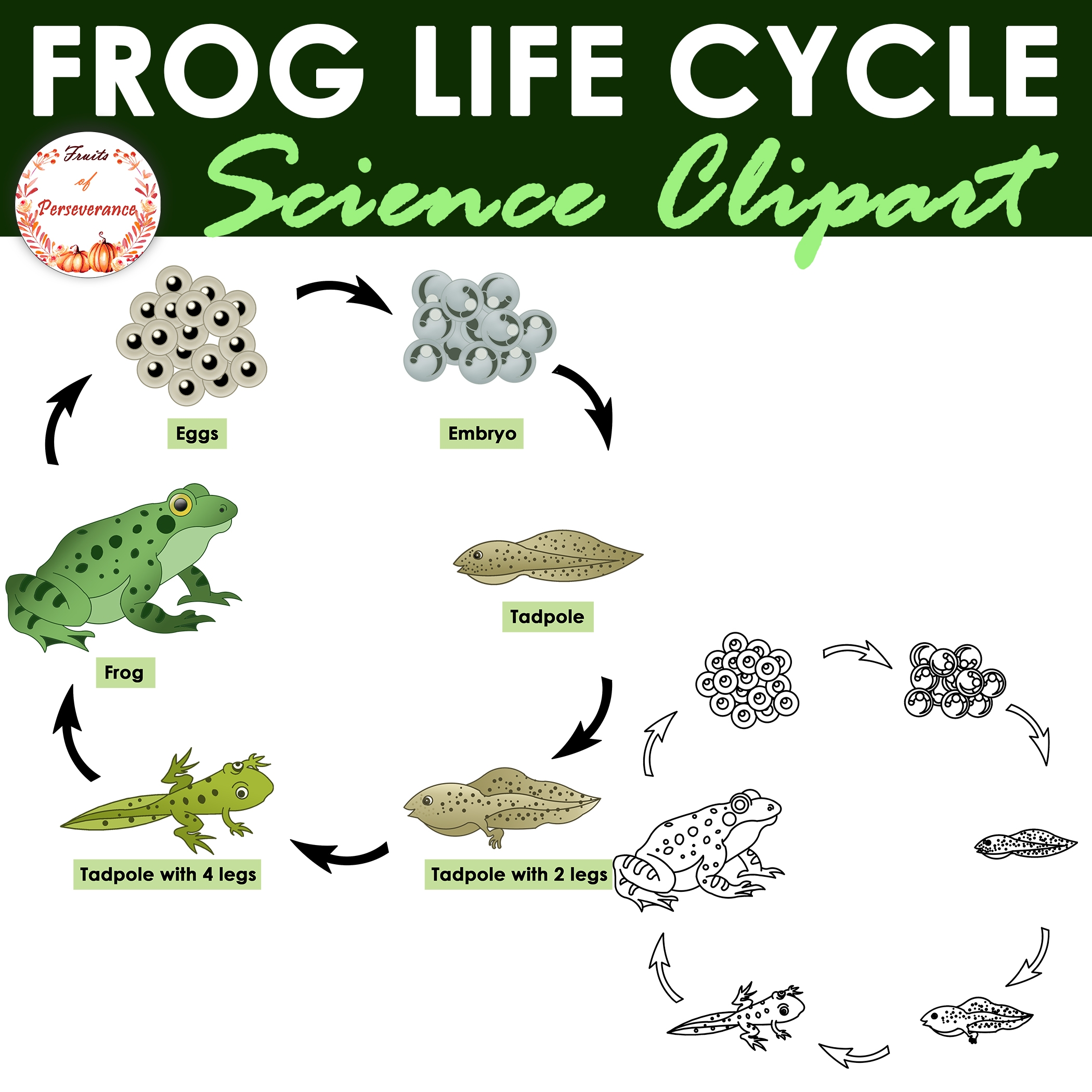
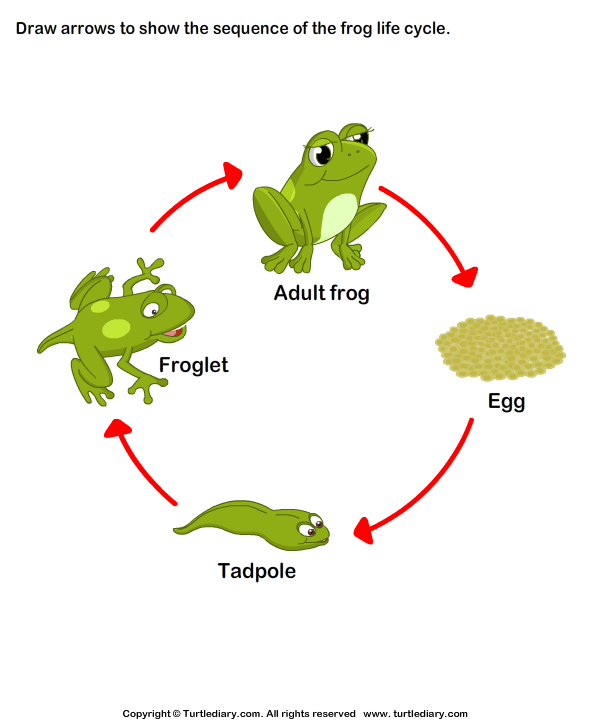
The life cycle of a frog begins with eggs. Female frogs lay eggs in water, which hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles have gills and tails, allowing them to swim and breathe underwater. As they grow, tadpoles develop legs and lose their tails.
Next, tadpoles undergo metamorphosis, transforming into froglets. Froglets have both lungs and gills, allowing them to breathe on land and in water. They continue to grow and develop until they reach adulthood.
Finally, the froglets mature into adult frogs. Adult frogs have fully developed lungs and legs for hopping on land. They also have specialized skin that helps them absorb water and oxygen. Adult frogs reproduce, completing the cycle by laying eggs and starting the process anew.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog is a fascinating journey from egg to adult. Each stage brings new changes and adaptations that allow frogs to thrive in their environment. By understanding the stages of a frog’s life, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of these amazing creatures.
In summary, the stages of the life cycle of a frog are an incredible example of nature’s wonders. From eggs to tadpoles to froglets and finally adult frogs, each phase plays a crucial role in the survival of these remarkable amphibians. Next time you see a frog, take a moment to marvel at the journey it has undertaken to reach adulthood.